News Highlights
Surat’s success in connecting 75 farmers in every panchayat with Natural Farming is going to become an example for the entire country.
Zero Budget Natural Farming
- Zero Budget Natural Farming (ZNBF) means raising crops without using any fertilisers and pesticides or any other external materials.
- The word Zero Budget refers to the zero cost of production of all crops.
- ZBNF guides the farmers towards sustainable farming practices thus helps in retaining soil fertility, to ensure a chemical free agriculture and ensure low cost of production (zero cost) and thereby enhancing the farmers income.
- In short, ZBNF, is a farming method that believes in growing crops in tune with nature.
Need of Zero Budget Natural Farming
- Increased cost of farm inputs
- National Sample Survey Office (NSSO) data indicates more than 50 per cent of all farmers are in debt due to increased cost of farm inputs like fertilizers and chemical pesticides.
- Objective of Doubling farmers’ income by 2022
- The farm expenditure needs to be brought down and natural farming practices like ZBNF have to be encouraged to reduce the dependence of the farmers on external inputs like chemical fertilizers, pesticides etc.
- High dependence on farm loans
- Zero budget farming model brings down farm expenditure to a great extent and ends dependence on farm loans.
- It also reduces dependence on purchased inputs as it encourages use of own seeds and locally available natural fertilizers and farming is done in synchronization with nature.
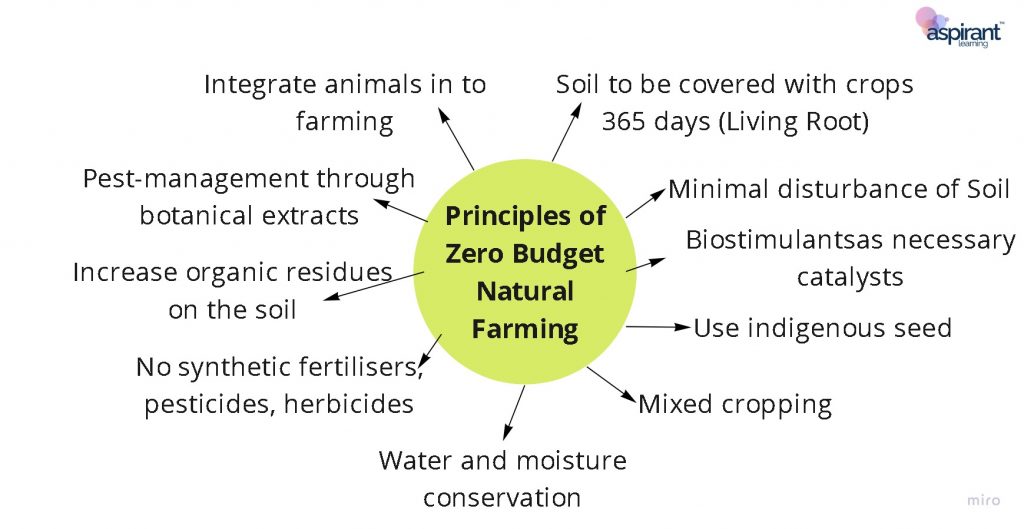
Principles of Zero Budget Natural Farming
Benefits of ZBNF
- ZBNF processes require 50–60 per cent less water and less electricity (than non-ZBNF) for all the selected crops.
- It reduces farmers’ costs through eliminating external inputs and using in-situ resources to rejuvenate soils
- ZBNF reduces methane emissions significantly through multiple aeration. It also has the potential to avoid residue burning by practising mulching.
- The cost of cultivation is lower in ZBNF.
Four main elements and models of ZNBF:
- Bijamrita:
- The seeds are treated with formulations prepared using cow dung and cow urine from native cow species.
- Jiwamrita/Jeevamrutha:
- Jiwamrita is prepared using cow dung and cow urine.
- It is a fermented microbial culture obtained from cow dung, urine, jaggery, pulse flour and uncontaminated soil.
- This fermented microbial culture, when applied to soil, adds nutrients to the soil besides acting as a catalytic agent to promote the activity of microorganisms and earthworms in the soil.
- Acchadana/Mulching:
- Mulching is the process of covering the top soil with crop wastes/organic waste or with cover crops.
- Waaphasa/Moisture (Soil Aeration):
- Good aeration is required in the soil for plant growth and development.
- Due to the application of Jiwamrita and mulching, the aeration of the soil increases, thus improves humus content, water availability, water holding capacity and soil structure which is most suitable for crop growth especially during drought periods.
Government Initiatives to promote ZBNF
- Paramparagat Krishi Vikas Yojana (PKVY)
- In the revised guidelines of PKVY scheme during the year 2018, various organic farming models like Natural Farming, Rishi Farming, Zero Budget Natural Farming (ZBNF) etc. have been included
- And also flexibility is given to states to adopt any model of Organic Farming including ZBNF depending on farmer’s choice.
- Rashtriya Krishi Vikas Yojana (RKVY).
- Under the RKVY scheme, organic farming/ natural farming project components are considered by the respective State Level Sanctioning Committee (SLSC) according to their priority/ choice.
Pic Courtesy: The Hindu
Content Source: Hindustan Times



