News Highlights
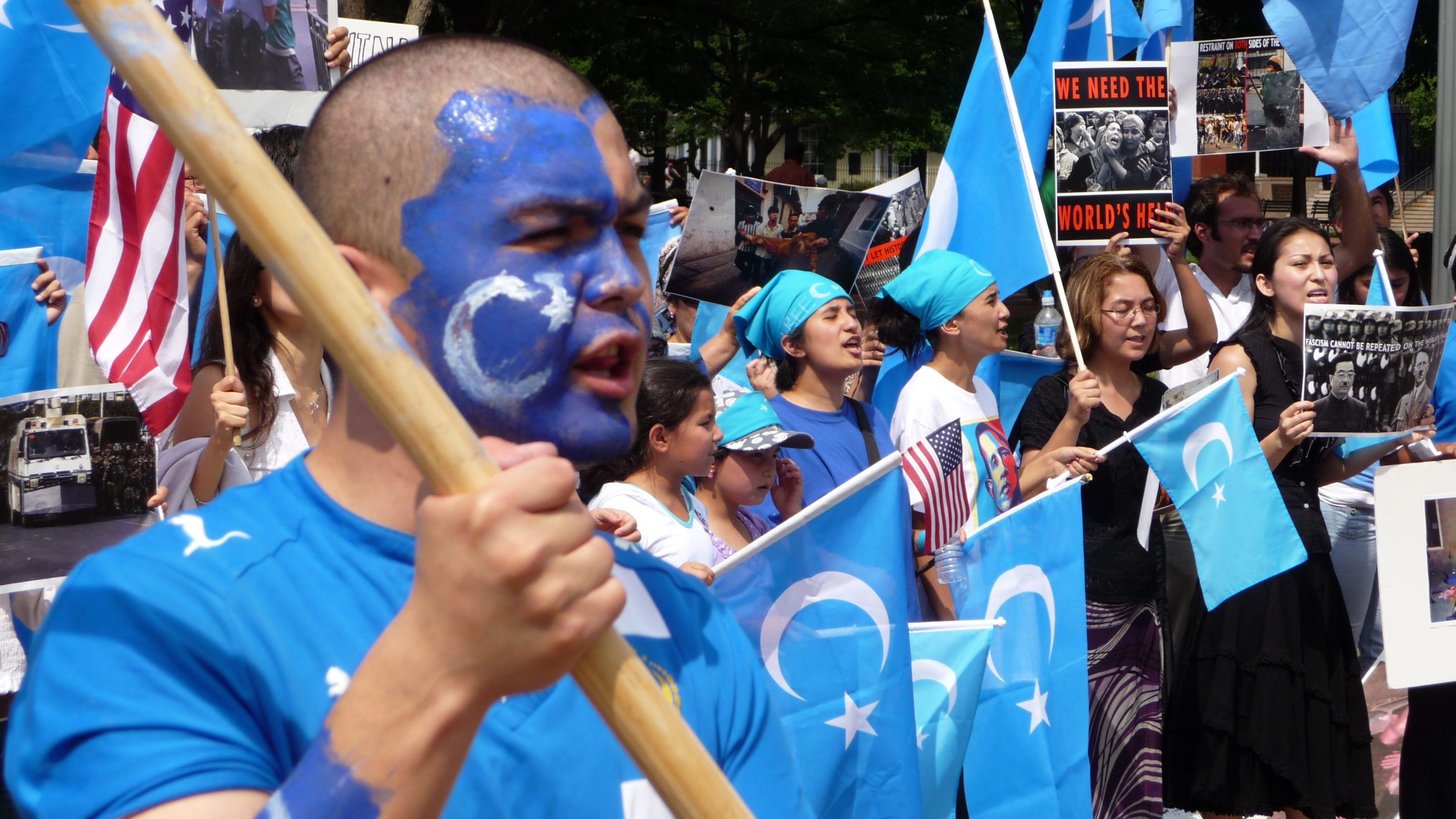
UN Human Rights in Xinjiang look into matters of Uighurs.
Who are Uighurs?
- The Uighurs are a Turkic ethnic group with roots in Central and East Asia that are primarily Muslim.
- The Uighurs speak a language that is similar to Turkish and consider themselves to be culturally and ethnically related to Central Asian countries.
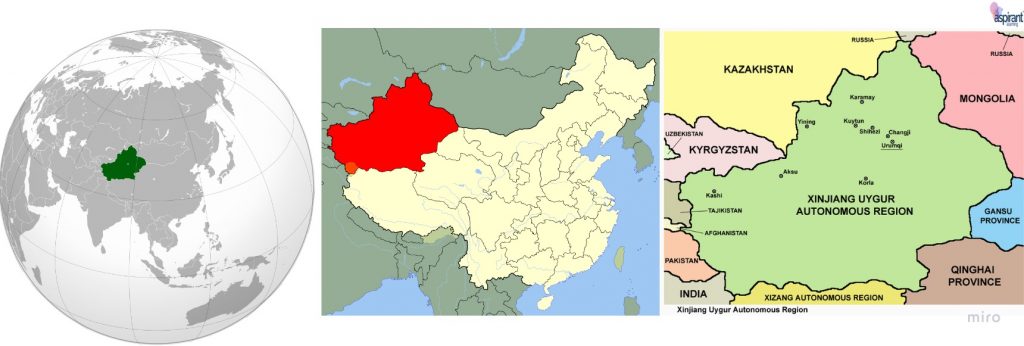
- The Xinjiang Uyghur Autonomous Region of the People’s Republic of China is where they were born.
- Other Parts of the World they live in – The United States, Australia, Canada, Germany, Sweden, Afghanistan, Norway, Turkey, Belgium, Russia, the Netherlands, and Saudi Arabia all have tiny Uyghur communities.
- The Uyghurs are one of China’s 55 officially recognized ethnic minority groups.
Threats Face by Uighurs
- Culture Difference
- The Uighurs are Muslim, do not speak Mandarin as their first language, and have a distinct ethnicity and culture from mainland China.
- Movement of Chinese Ethnic People to Xinjiang
- As economic prosperity has spread over Xinjiang in recent decades, it has brought with it a massive influx of Han Chinese, who have snatched up the better professions, leaving the Uighurs fearful for their livelihoods and identity.
- This resulted in intermittent violence, culminating in a riot in Urumqi in 2009 that killed 200 people, predominantly Han Chinese.
- Detention on Uighurs
- According to sources, the Chinese government has arrested over a million Uyghur Muslims in Xinjiang re-education facilities since 2016.
- The fundamental goal of these re-education camps was to ensure that people followed the Chinese Communist Party’s ideology.
- For decades, Uighur Muslims have been persecuted, imprisoned, scrutinized, spied on, and even sold into slavery.
- Chinese Acquisition on Uighurs
- China claims that the Uighur people want to build their own country, and because of the Uighurs’ cultural ties to their neighbours, Chinese policymakers are afraid that separatist activities in Xinjiang could be backed by Pakistani elements.
China is Being Blamed.
- Forced labour, systematic forced birth control, torture, and the separation of children from jailed parents have all been charged of Chinese officials.
- Several countries, including the United States, Canada, and the Netherlands, have charged China of genocide, which is defined as the “desire to exterminate, in whole or in part, a national, ethnical, racial, or religious group” under international convention.
- To control the population, China has been forcefully sterilizing Uyghur women, taking children from their families, and seeking to disrupt the group’s traditional traditions.
- In 2018, a UN human rights committee stated it received reliable evidence that China was detaining up to a million individuals in Xinjiang’s “counter-extremism centers.”
- In 2020, the Australian Strategic Policy Institute discovered evidence of China than 380 “re-education camps” in Xinjiang, up 40% from prior estimates.
Reasons for Crack Down
- Since the 1990s, anti-Han and separatist sentiment has grown in Xinjiang, occasionally erupting in bloodshed.
- Around 200 people were killed in Xinjiang violence in 2009, which the Chinese blamed on Uighurs seeking their own state.
China’s Stand
- China denies any charges of human rights violations in Xinjiang, arguing that its “re-education” camps are in place to combat separatist and Islamist militancy.
- It has consistently denied allegations of ethnic cleansing in Xinjiang against Uighurs and other Muslim Turkic people.
- China accused the United States, France, and the United Kingdom of having a “poor human rights record.”
Global Response on Uyghur Issue
- A number of Muslim countries, including Saudi Arabia, the United Arab Emirates, Egypt, and Pakistan, have refrained from criticizing China for its treatment of the Uighurs, opting instead to work with China on a variety of issues, including deportation.
- Since 1952, the Turkish government has granted Uighurs shelter.
- The United States has raised concerns about Chinese crimes in Xinjiang and elsewhere.
- Human Rights Watch issued a report in 2017 urging the Chinese government to release the detainees and close the political indoctrination centers immediately.
India’s Response
- The Indian government has been deafeningly quiet about the Uyghur problem.
About Xinjiang
- Xinjiang is a landlocked autonomous region of China, located in the northwest of the country near Central Asia.
- Borders – Mongolia, Russia, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, Afghanistan, Pakistan, and India all border Xinjiang.
- Other Details
- Much of Xinjiang’s boundaries, as well as its western and southern parts, are dominated by the mountainous Karakoram, Kunlun, and Tian Shan mountain ranges. India claims the Aksai Chin and Trans-Karakoram Tract regions, both controlled by China.
- Xinjiang shares boundaries with Tibet Autonomous Region, Gansu, and Qinghai provinces.
- From the east to the northern boundary, the most well-known Silk Road path passed through the area.
Way Forward
- As in the present situation of rough weather with China , India should continue to present stand of neutrality in this issue.



