News Highlight
El Nino on its way, will likely impact monsoon: Experts
Key Takeaway
- An El Nino event in the equatorial Pacific Ocean may occur sooner than expected, as several climate models predict an El Nino as early as May 2023.
- The emergence of an El Nino in May or June could weaken the southwest monsoon season.
- It accounts for over 70% of total rainfall in India, on which most farmers continue to rely.
- Heatwaves and droughts could also occur in India and other parts of the planet, including South Africa, Australia, Indonesia, and the Pacific Islands.
- It brings significant rainfall and flooding to other locations, including California in the United States, and may cause coral reef bleaching and death.
El Nino
- About
- El Nio is an approximate translation of the Spanish words “small boy” or “Christ child.”
- It was previously known as “El Nio de Navidad” since it peaks around December.
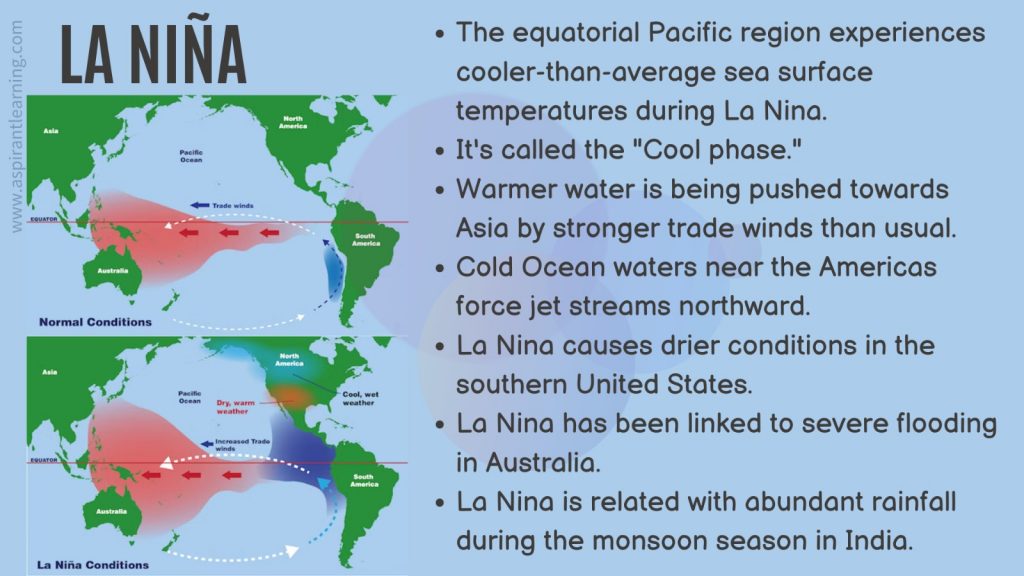
- El Nio is a periodic warming of sea waters in the Central-East Equatorial Pacific (Warm phase off the coast of Peru).
- Surface temperatures in the equatorial Pacific rise during El Nio.
- This weakens the trade winds, which blow east-west near the Equator.
- Because of El Nio’s easterly trade winds that blow from the Americas to Asia change direction and become westerlies.
- As a result, it transports warm water from the western Pacific to North America.
Effects of El Niño Phenomenon
- Weather
- El Nio brings a dry, warm winter in the northern United States and Canada.
- As well as greater flooding risk along the Gulf Coast and in the southeastern United States.
- Drought affects Indonesia and Australia.
- In India, an El Nino event is significantly associated with reduced monsoon rainfall.
- Marine resource
- El Nio reduces upwelling (the rise of deeper waters to the surface), which reduces phytoplankton off the coast.
- Fish that consume phytoplankton are the first to be harmed, followed by creatures higher up the food chain.
- Warm water
- Warming water transports tropical species northward, affecting diverse ecosystems.
- Airflow above the ocean
- Heat redistribution on the ocean’s surface affects airflows above the sea.
El Nino – Impacts on India
- The Indian monsoon and El Nino have an inverse connection.
- Six of India’s most notable droughts since 1871 have been El Nino droughts, including the most recent ones in 2002 and 2009.
- Yet, not every El Nino year in India ended in a drought.
- For example, despite a major El Nino year in 1997/98, there was no drought.
- It’s because of the Indian Ocean Dipole.
- In contrast, a weak El Nino in 2002 caused one of the worst droughts on record.
- El Nino directly impacts India’s agricultural industry because it affects the output of summer crops like rice, sugarcane, cotton, and oilseeds.
- The result is high inflation and sluggish GDP growth, as agriculture accounts for roughly 14% of the Indian economy.
El Nino-Southern Oscillation (ENSO)
- About
- The tropical South Pacific Ocean typically has high pressure, while the tropical Indian Ocean has low pressure.
- This pressure pattern, however, can be inverted, resulting in low pressure in the Pacific and high pressure in the Indian Ocean.
- This is the Southern Oscillation, a periodic change in pressure conditions.
- The El Nino phenomenon is linked to these fluctuations in pressure conditions forming in the Pacific and Indian seas.
- The El Nino Southern Oscillations, or ENSO, are related phenomena.
Measuring Technique of El Nino
- A buoy is a floating object that serves as a navigational aid or warning signal for ships in the middle of the ocean.
- They are typically vibrantly coloured (fluorescent).
- These buoys measure temperatures, currents, winds, and humidity.
- Regularly, the buoys send data to researchers and forecasters across the world.
- It enables scientists to predict El Nino better and see its evolution and impact worldwide.
- The Oceanic Nino Index (ONI) is a technique used to calculate deviations from average sea surface temperatures.
- The Oceanic Nino Index measures the deviation of sea surface temperature from normal in the east-central Pacific Ocean.
- It is the fundamental approach for predicting, determining, and evaluating each El Nino episode.
Conclusion
- The presence of warm ocean surface waters off Ecuador and Peru’s shores is called El Nino.
- The regular upwelling of cold, nutrient-rich deep ocean water is considerably reduced when this occurs.
- El Nino often happens around Christmas and lasts several weeks to several months.
- El Nino is not a consistent cycle that can be forecasted in the same way that ocean tides can.
Pic Courtesy: SNE
Content Source: Down to Earth