News Highlights:
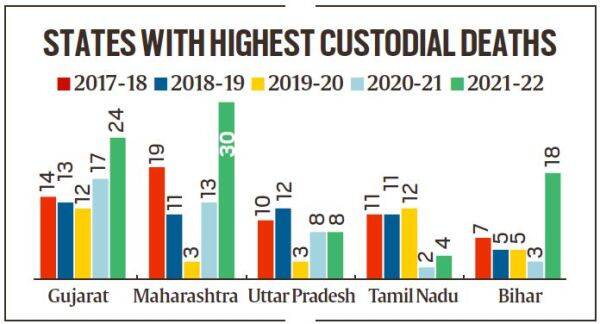
- according to data by the Union Ministry of Home Affairs, in the Rajya Sabha, Gujarat witnessed the most number of custodial deaths in the last five years with 80 such cases, followed by Maharashtra with 76 deaths and Uttar Pradesh with 41 deaths.
- Tamil Nadu is fourth on the list with 40 deaths and Bihar is fifth with 38 cases.
Custodial violence:
- About:
- Custodial violence primarily refers to violence in police custody and judicial custody. Custodial violence, which includes torture, death and other excesses in police custody or prison.
- Most of the custodial deaths were attributed to reasons other than custodial torture, which included suicide and death in hospitals during treatment
- One of the biggest issues with custodial violence is that it has put human rights at stake. This crime is an outburst against humanity and is one of the many root obstacles in a Democratic country
- According to the Law Commission of India, the crime by a public servant against the arrested or the detained person who is in custody amounts to custodial violence.
- Custodial deaths in India:
- Custodial deaths in India may refer to the deaths of persons in police custody and also to the deaths of persons in judicial custody while undergoing trial or serving a sentence.
- In the financial year 2021–22, the National Human Rights Commission of India reported 2152 deaths had occurred in judicial custody, and 155 deaths had occurred in police custody till 28 February 2022.
- According to a report released by National Campaign Against Torture (NCAT), there were 1606 deaths in 2019 which occurred in judicial custody, and 125 death occurred in police custody.
- 4484 cases of custodial deaths were reported in India during the period FY 2020-21 to FY 2021-22.
Legal protections:
- Constitutional provisions:
- Article 20 (3) of the Indian Constitution protects the citizens from self-incrimination. Self-incrimination is the act of implicating or exposing one’s own self to criminal prosecution. No person accused of any offence shall be compelled to be a witness against himself.
- Article 21 states that “No person shall be deprived of his life or personal liberty except according to procedure established by law”. Protection from torture is a fundamental right enshrined under Article 21 (Right to Life) of the Indian constitution.
- Article 22 provides “Protection against arrest and detention in certain cases”. The right to counsel is also a fundamental right under Article 22(1) of the Indian constitution.
- Code of Criminal Procedure:
- Section 176 (I) of the Code of Criminal Procedure (CrPC) states that if a person in custody dies or disappears or a woman is raped in custody, the Judicial Magistrate has the power to order an inquiry.
- Section 46 of the Code of Criminal Procedure (CrPC) states the police cannot kill anyone while performing an arrest.
- Section 49 of the Code of Criminal Procedure (CrPC) states the police cannot use excessive restraints while performing an arrest.
- Section 54 of the Code of Criminal Procedure (CrPC) allows the Magistrate to appoint a medical petitioner to examine the accused under trial.
- Indian Penal Code (IPC):
- Sections 330 (a) and (b) of the Indian Penal Code (IPC) allow sentences of up to 7 years for policemen in cases of torture.
- Indian Evidence Act, 1872:
- Articles 24 and 25 of the Indian Evidence Act of 1872 render forced confessions and confessions made to the police irrelevant in trials.

Reasons for Custodial Violence in India:
- Lack of Strict Rules:
- It is essential that strict and mandatory laws are passed to stop custodial violence.
- In India, custodial violence is yet to be criminalised, and an unfair benefit of which has been taken by those in power over the past many decades
- No Substantial Prison Reform:
- The entire prison system is inherently opaque, giving less room for transparency.
- Prisons in India continue to be affected by poor conditions, overcrowding, acute manpower shortages and minimal safety against harm in prisons
- Work Pressure
- The police work under extreme pressure and in cases of a quick solution to complex cases, they choose violence to get evidence and confessions
- Social Factor
- Considering the approach of “an eye for an eye”, the people in power choose to use violence to get out information from the ones accused of a crime
- Failure to adhere to international standards:
- India had signed the United Nations Convention against Torture in 1997, but its implications are yet to be mandatorily followed in the country
Conclusion:
- Proper reforms must be implemented to completely prohibit custodial and judicial violence.
- India should ratify the UN Convention Against Torture as it will mandate a systematic review of the colonial methods, practices and arrangements for the custody and treatment of persons subjected to arrest, detention or imprisonment.
- The police officials must be trained under special guidelines so that any kind of violence can be prevented
Pic Courtesy: Freepik
Content Source: The Indian Express



