News Highlight
Monitoring the evolution of the shapeshifting bird flu virus can add to the preparedness against another potential pandemic.
Key Takeaway
- Bird flu, often known as avian influenza, is a highly contagious viral virus that mainly affects birds.
- The virus can infrequently infect mammals from birds, a condition known as spillover, and it can only rarely transfer between mammals.
Bird flu Virus
- About
- Avian influenza, sometimes known as bird flu, is a disease caused by avian influenza.
- Additionally, type A viruses are naturally prevalent in wild birds worldwide.
- The virus can infect household fowl such as chickens, ducks, and turkeys, and there have been reports of H5N1 infection in Thailand zoos in pigs, cats, and even tigers.
- The two proteins on the surfaces of Avian Influenza type A viruses are used to classify them: Hemagglutinin (HA) and Neuraminidase (NA).
- Furthermore, there are approximately 18 HA and 11 NA subtypes. H5N1, H7N2, H9N6, H17N10, and other combinations of these two proteins are feasible.
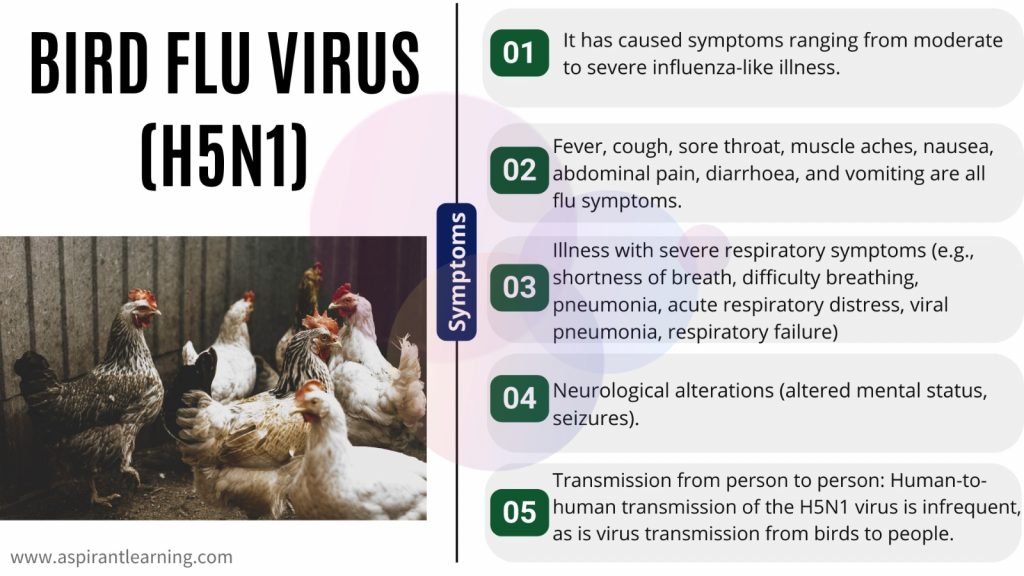
- Bird flu: Infection in humans
- Firstly, human infections with avian and swine influenza strains such as A(H1N1), A(H1N2), A(H5N1), and A(H7N9) have been reported.
- The first human H5N1 infection was identified in 1997.
- Over 700 instances of Asian Highly Pathogenic Asian Avian Influenza A (HPAI) H5N1 virus infection have been reported to the World Health Organization from 16 countries.
- As well as, the infection is lethal, with a fatality rate of around 60%.
- Furthermore, direct contact when a person comes into close touch with infected birds, either dead or living, is the most prevalent method of virus transmission.
Modes of Transmission of Avian Influenza
- Avian influenza is typically disseminated through direct contact between infected and healthy birds.
- In addition, it can be detected in secretions from the nose, mouth, and eyes, among other places.
- HPAI illness is transmitted to humans by diseased chickens; the sickness is not airborne.
- Humans can transmit the avian influenza virus from birds, although human-to-human contact is considerably more difficult without symbolic interaction.
- The following man-made habitats have helped spread avian influenza:
- Indoor commercial poultry
- Range-raised commercial poultry
- Live poultry markets
- Hobby flocks
- Bird collection and trading systems
Impact of Avian Influenza
- Firstly, member states of The WHO have recognised the necessity for a transparent framework for exchanging vaccines and gaining advantages from other networks.
- Cooperative initiatives developed in response to HPAI have served as the foundation for programmes addressing other emerging and re-emerging infectious illnesses.
- The poultry sector provides around 20% of the protein consumed.
- Additionally, periodic bird flu epidemics impact poultry consumption because diseased birds are culled in huge numbers.
- In Vietnam, 50 million birds were slaughtered as part of infection control operations.
- According to a Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) estimate, economic losses in South East Asia totalled over US$ 10 billion.
- Small commercial producers feel the most significant impact.
- Furthermore, the government’s compensation for the lost chickens has changed over time. ‘Some were paid significantly less than the market wage, while others received no pay.
Pic Courtesy: The Hindu
Content Source: The Hindu



