News Highlights:
Recently, the Bombay High Court set aside the writing down of Yes Bank’s Additional Tier 1 Bonds worth around Rs 8,400 crore.
Key Takeaway:
Earlier, the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) proposed to write down Additional Tier-1 (AT-1) bonds as part of the SBI-led restructuring package for Yes Bank.
Additional Tier 1 (AT-1 Bonds):
- About:
- AT-1 bonds are unsecured, perpetual bonds that banks issue to shore up their core capital base to meet the Basel-III norms.
- These bonds don’t have any expiry date and are issued to raise long-term capital.
- Background:
- AT-1 bonds were first conceptualised following the disastrous global financial crisis of 2008 when many banks were closed down.
- Key Points on AT 1 bond:
- AT-1 bonds are like standard bonds but have a comparatively higher interest rate.
- They are also listed and traded on stock exchanges.
- This means that the person holding the bond can sell it in secondary marketing if funds are required.
- Banks issuing AT-1 bonds can even reduce the bonds’ face value.
- AT-1 bonds are regulated by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI).
- If there is a need for RBI to bail out a bank, it can tell the bank to write off its outstanding AT-1 bonds without necessarily consulting its investors.
- Investors cannot return these bonds to the issuing bank and get the money. i.e. there is no put option available to its holders.
- How to acquire AT 1 bond:
- There are two routes through which these bonds can be acquired:
- Initial private placement offers of AT-1 bonds by banks seeking to raise money.
- Secondary market buys of already-traded AT-1 bonds.
- There are two routes through which these bonds can be acquired:
- Norms that regulate AT-1 Bonds:
- Basel III regulates AT-1 Bonds.
- Basel III norms require Indian banks to maintain a capital ratio of 11.5% divided into 8% in tier 1 capital and tier 2 capital.
- It should be noted that AT-1 bonds are known as “unsecured subordinated perpetual non-convertible bonds” that constitute a component of a bank’s permanent capital.
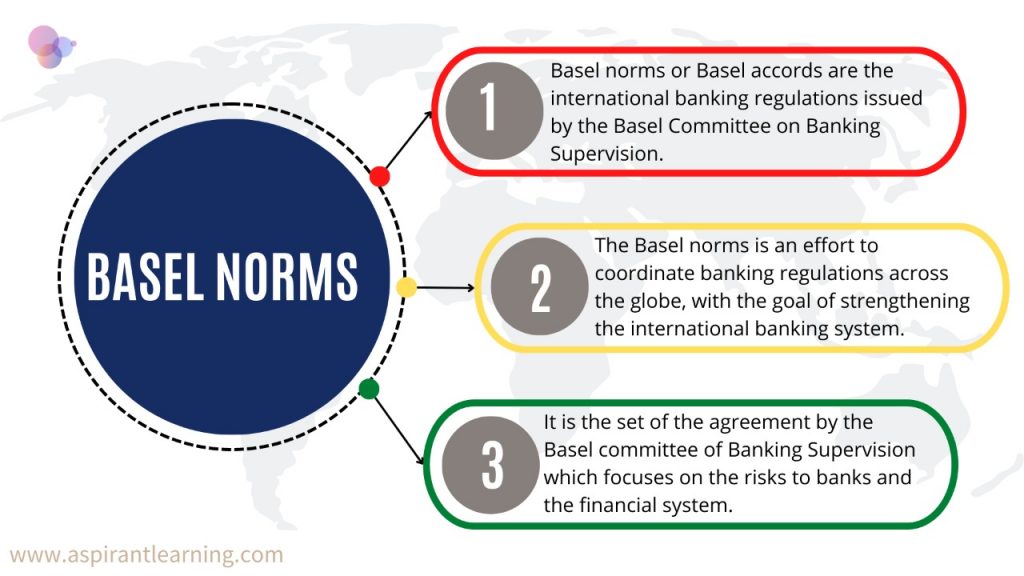
Basel-III Norms:
- About:
- Basel III Norms are an international regulatory accord that has introduced reforms, ensuring improved regulation and supervision in the banking sector.
- Under the Basel-III norms, banks were asked to maintain a certain minimum level of capital and not lend all the money they receive from deposits.
- According to Basel-III norms, banks’ regulatory capital is divided into Tier 1 and Tier 2, while Tier 1 is subdivided into Common Equity Tier-1 (CET-1) and Additional Tier-1 (AT-1) capital.
- Common Equity Tier 1 capital:
- Common Equity Tier 1 capital includes equity instruments where returns are linked to the banks’ performance and, therefore, the share price performance.
- They have no maturity.
- Additional Tier-1 capital:
- Additional Tier-1 capital is perpetual bonds which carry a fixed coupon payable annually from past or present profits of the bank.
- They have no maturity, and their dividends can be cancelled anytime.
Pic Courtesy: Freepik
Content source: The Indian Express



