News Highlights:
- NASA’s James Webb telescope takes pictures of rings around Uranus.
- In 2022, Webb took the clearest image of Neptune, its rings and its Moons.
James Webb Space Telescope:
- About:
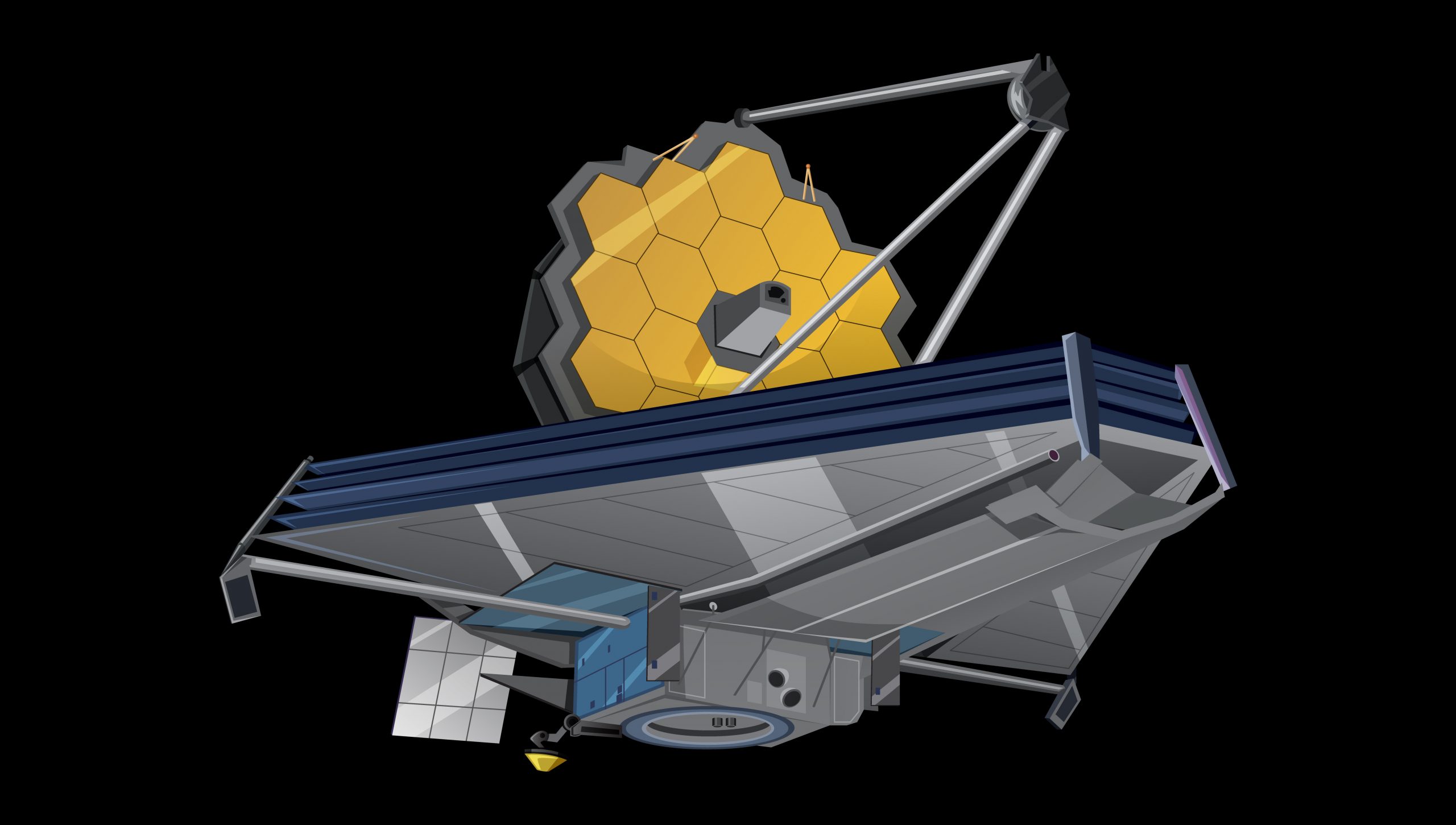
- The James Webb Space Telescope is the next-generation space observatory succeeding the Hubble Space Telescope. It is designed to unlock the answer to unsettled questions about our Universe.
- The telescope is the result of an international collaboration between NASA, the European Space Agency (ESA) and the Canadian Space Agency which was launched in December 2021.
- Location:
- It is currently at a point in space known as the Sun-Earth L2 Lagrange point, approximately 1.5 million km beyond Earth’s orbit around the Sun.
- Lagrange Point 2 is one of the five points in the orbital plane of the Earth-Sun system.
- Named after Italian-French mathematician Josephy-Louis Lagrange, the points are in any revolving two-body system like Earth and Sun, marking where the gravitational forces of the two large bodies cancel each other out.
- Objects placed at these positions are relatively stable and require minimal external energy or fuel to keep themselves there, and so many instruments are positioned here.
- Key Features:
- It’s the largest, most powerful infrared space telescope ever built.
- It’s the successor to Hubble Telescope.
- It can see backwards in time to just after the Big Bang by looking for galaxies that are so far away that the light has taken many billions of years to get from those galaxies to our telescopes
Goals of James Webb Space Telescope:
- Detecting First Galaxies and Planets Formed After Big Bang:
- After the Big Bang, the whole Universe is in a state of expansion.
- So the first galaxies and stars are undoubtedly the farthest objects in the known Universe.
- Hubble’s Law states that the more distant the objects, the faster they move away from us.
- Therefore, the light from the oldest celestial bodies is always redshifted. Ordinary telescopes can’t efficiently detect such faint objects. In order to detect such objects, we should look into the infrared band.
- The James Webb Space Telescope is purposefully designed to observe objects hidden in the infrared spectrum.
- Observing the Formation of Galaxies:
- One of the main aims of JWST is to study and observe the formation of galaxies.
- As per current data, we cannot detect any region where baby galaxies are forming.
- In other words, such areas might be far away from the reaches of the current most sensitive observatories.
- Through the Webb telescope, astronomers hope to analyse the factors that influence galaxies’ shape and size.
- It will shed light on the secrets behind the structure of barred, irregular, elliptical, and spiral galaxies.
- Star Formation in Nebulae
- Stars are usually created from a nebula, a region with high-density dust and gas particles.
- Huge streams of dust particles surround the baby stars, which block most of the normal visible light emitted.
- Fortunately, infrared from baby stars penetrates through the dust barrier. Therefore, powerful infrared observatories like the James Webb Space Telescope should be able to observe them.
- Observing Exo-planets
- Two of the central ambitions of JWST are to find the origin of Earth and how life evolved.
- Both are directly connected to the evolution of planets.
- One of the fundamental goals is to find the composition of particles around stars where planets are created.
- Hypersensitive observatories like the JWST will be able to capture infrared images of planet systems.
- Search for alien life forms is one of its hidden missions.
- A thorough exploration of exo-planets will help us understand how life could have evolved.
- JWST is powerful enough to examine comets and other cold bodies, which might hold clues to the origin of life.
Pic Courtesy: Freepik
Content Source: The Indian Express