News Highlight
Skyroot Aerospace successfully test-fires a 3D-printed cryogenic engine for a record 200 seconds.
Key Takeaway
- In a private propulsion test facility, the first Indian private company to fly a rocket into space successfully tested a completely cryogenic rocket engine.
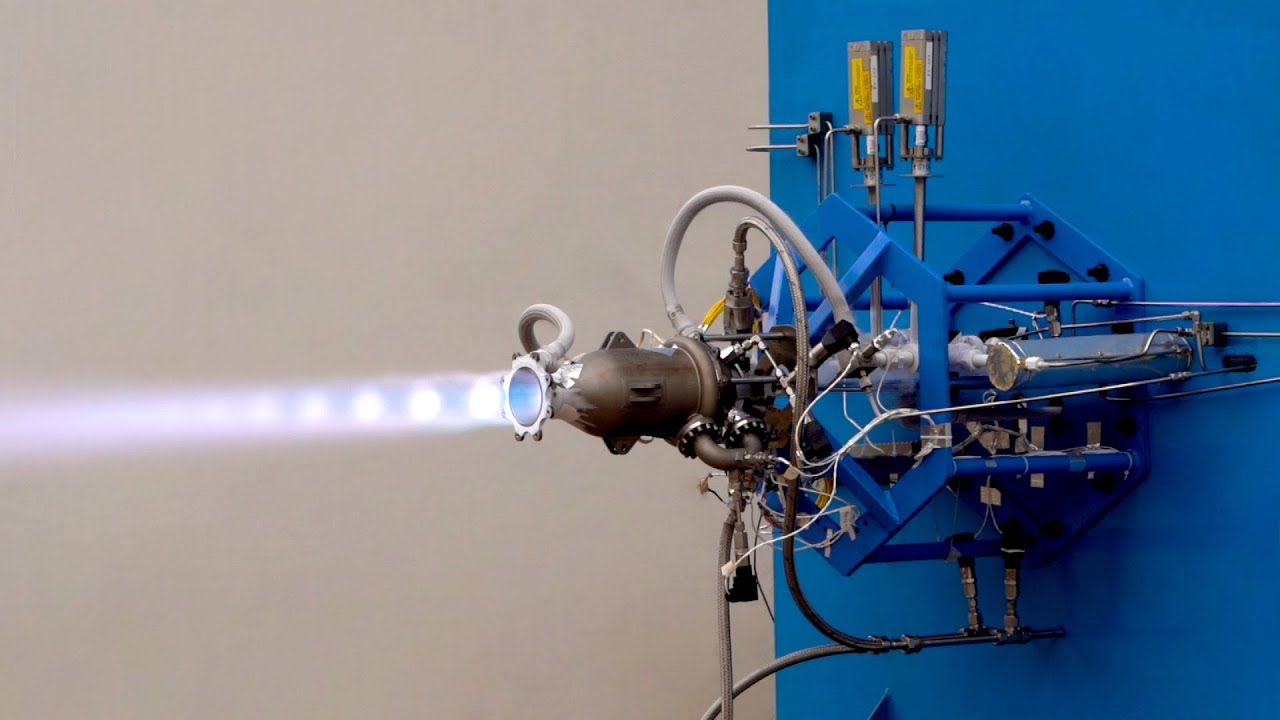
- Skyroot Aerospace, a pioneering private rocket builder, accomplished a significant milestone by successfully testing-firing a sophisticated, entirely 3D-printed cryogenic engine for a record 200 seconds.
- The ‘Dhawan-II endurance test was conducted at Solar Industries’ propulsion test facility in Nagpur, Maharashtra, using an indigenously constructed mobile cryogenic engine test pad.
- This accomplishment comes on the heels of the November 2022 launch of Vikram – S.
- It marked the company as the first Indian private corporation to launch a rocket into space.
- The Dhawan-II engine expands on the firm’s first privately developed fully-cryogenic rocket engine, the 1.0 kN thrust Dhawan – I.
- It was successfully test launched on November 21.
Cryogenic Engine
- About
- A cryogenic engine or cryogenic stage is the final stage of a space launch vehicle that uses cryogenics.
- Cryogenics is the study of the manufacture and behaviour of materials at shallow temperatures (less than -150°C) to lift and deploy heavy objects in space.
- Its propellants are liquid oxygen (LOx) and liquid hydrogen (LH2).
- They are one of the most difficult to develop, and only six countries have them so far: the United States, China, Russia, France, Japan, and India.
- Cryogenic fuel is used in the upper stage of India’s biggest launch vehicles, the GSLV and GSLV Mk III.
- Advantages
- When compared to solid and earth-storable liquid propellant rocket stages.
- It is more efficient and generates more thrust per kilogramme of fuel burned.
- Utilising a cryogenic upper stage instead of a solid fuel stage increases a rocket’s payload-carrying capabilities.
- Both fuels (LOx and LH2) are less environmentally harmful than solid, semi-cryogenic, and hypergolic fuels in the rocket business.
- Disadvantage
- It is a far more sophisticated system than solid/earth-storable liquid propellant stages.
- It is due to using fuels at shallow temperatures and the resulting thermal and structural issues.
3D Printing
- About
- 3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing.
- It is a technique that employs materials such as plastics and metals to turn computer-aided design goods into genuine three-dimensional items.
- It is the inverse of subtractive manufacturing.
- For example, it involves cutting/hollowing out a piece of metal or plastic with a milling machine.
- 3D printing has traditionally been used for prototyping and has many applications.
- It includes the creation of artificial limbs, stents, dental crowns, vehicle parts, and consumer goods.
Dhawan II
- About
- Skyroot’s Dhawan cryogenic engine series is named after Satish Dhawan.
- It is a renowned Indian rocket scientist who was instrumental in establishing India’s space programme.
- Skyroot’s first privately developed fully-cryogenic rocket engine, Dhawan-I, was successfully test-launched in 2021, and Dhawan II expands on that.
- It is entirely indigenous, and the engine was 3D printed using a superalloy, which cut manufacturing time by 95%.
- It will be propelled by liquid natural gas (LNG) and liquid oxygen (LoX).
- LNG, which contains more than 90% methane, is seen as the future rocket fuel.
- The ANIC-ARISE programme of NITI Ayog helped to fund some of the engine development.
- It encourages innovations such as green rocket propellants.
Significance of Privatisation of the Space Sector
- The global space economy is valued at approximately USD 360.1 billion, with India accounting for barely 2% of the space economy.
- The industry’s commercial actors have been limited to serving as vendors/suppliers to the government’s space programme.
- Non-Governmental Entities (NGEs) increased participation in the space sector will increase India’s market share in the Global Space Economy.
- By promoting the private sector, the Indian space programme will be able to remain cost competitive in the global space market.
- As a result, countless employment will be created in space and other associated industries.
- This will assist India in cementing its position as a global leader in space technology and innovation.
- Private actors can introduce new technology, creativity, and management skills to space-related activities, resulting in cost savings and enhanced efficiency.
- This will also allow the government to focus on other crucial sectors.

Pic Courtesy: Circuit Digest
Content Source: The Hindu