News Highlight
Push development, integration of directed energy, hypersonic weapons: IAF Chief.
Key Takeaway
- Several countries have tested and used Directed Energy Weapons (DEWs) and Hypersonic Weapons.
- To achieve the needed range and accuracy, India’s defence companies must advance the development of these weapons and incorporate them into its airborne systems.
DEWs and Hypersonic Weapons
- About
- In layman’s terms, a directed-energy weapon harms or destroys its target by focusing energy using lasers, microwaves, or particle beams.
- Microwave weapons, laser weapons, drone defence systems, and so on are examples.
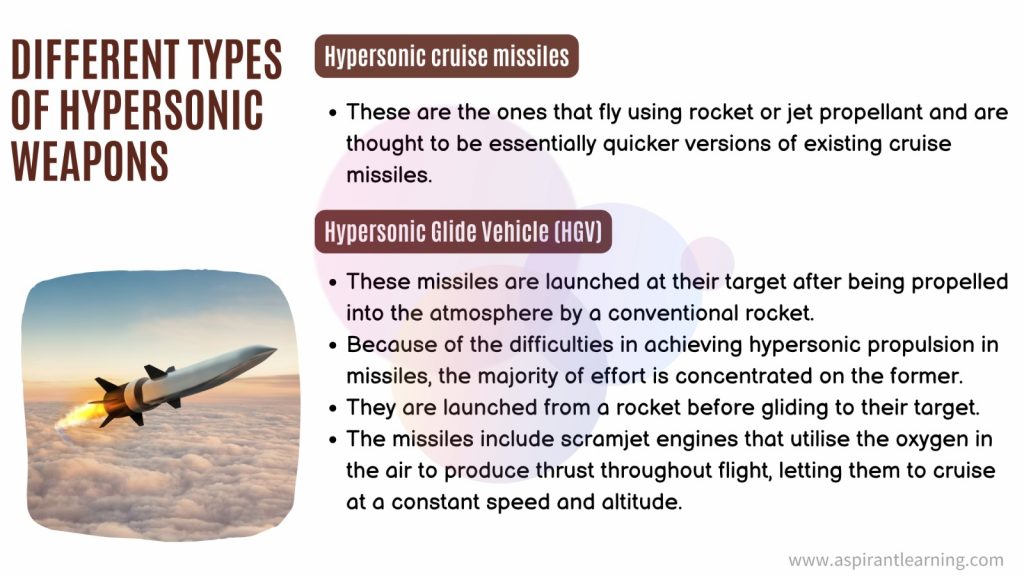
- A hypersonic weapon can attack its target at five to ten times the speed of sound (Mach 5 to Mach 10).
- Advantages of DEWs over Conventional Ammunitions
- DEWs, particularly lasers, have excellent precision, low cost per shot, logistical advantages, and are difficult to detect.
- They can transmit lethal force at the speed of light (about 300,000 kilometres per second).
- The forces of gravity or atmospheric drag do not constrain their beams.
- The type and intensity of energy directed to targets can be varied to adjust their effects.
Disadvantages of DEWs and Hypersonic Weapons
- Limited Range
- Most DEWs have a limited range, and their effectiveness diminishes significantly as the distance between the target and the weapon grows.
- High Cost
- They can be costly to research and construct, and their usefulness in particular scenarios may not justify the expense.
- Countermeasures
- DEWs can be mitigated using reflective materials or other countermeasures, although their effectiveness will be reduced.
- Arms Race
- When one government develops hypersonic weapons and DEWs, it sparks an arms race as other countries rush to create hypersonic weapons.
- This can exacerbate tensions and instability.
Significance for India
- The deployment of these technologies in the aerospace industry can potentially change how wars are fought, allowing India to compete.
- Its mission is to develop cutting-edge platforms, weapons, sensors, and networks to fight and win future wars.
- Improving India’s defence capabilities could deter hostile nations such as China and Pakistan.
Countries that have Hypersonic Technology
- Russia
- It is an Avangard glide vehicle that reportedly carries a nuclear payload and will be fired from an intercontinental ballistic missile.
- China
- Throughout the summer, its military conducted at least two hypersonic weapons tests.
- It includes the launch into space of an orbiting hypersonic weapon capable of carrying a nuclear warhead.
- China successfully tested the DF-17, a medium-range ballistic missile designed to deliver hypersonic glide vehicles.
- U.S.A
- The US Navy is leading the development of a glide vehicle used by all armed branches, while the Air Force is working on an air-launched glider.
- India
- Hypersonic technologies have been developed and tested by DRDO and ISRO.
Significance of hypersonic weapons
- They are typically classified as fast, low-flying, and highly manoeuvrable weapons that are too fast and nimble for standard missile defence systems to identify quickly.
- Unlike ballistic missiles, they do not follow a fixed, arched trajectory and can manoeuvre on their way to their target.
- They are adamant about defending against using existing defences.
India’s DEWs and Hypersonic Technology Projects
- 1KW laser Weapon
- DRDO has tested a 1KW laser weapon which hit a target 250m away.
- Directionally Unrestricted Ray-Gun Array (DURGA) II
- The DRDO has launched the DURGA II project, a 100-kilowatt lightweight DEW.
- Hypersonic Technology Development
- The DRDO and the ISRO have developed and tested hypersonic technologies in India.
- The Hypersonic Technology Demonstration Vehicle (HSTDV) can travel at 6 times the speed of sound.
- It was successfully flight-tested by DRDO in 2021.
- India is also developing an indigenous, dual-capable hypersonic cruise missile as part of its HSTDV Program.
Way Forward
- Atmanirbharta, or self-reliance in defence, could include creating indigenous designs and development skills through Indian security.
- We can expand investment in defence research and development to improve our defence strength.
Pic Courtesy: Department of Defence
Content Source: Indian Express



