News Highlight
The Rajasthan Right to Health Bill, 2022 was introduced to protect and fulfil equitable rights in health and well-being.
Key Takeaway
- The Rajasthan Assembly’s just concluded Budget Session reignited controversy over the Right to Health Bill.
- The proposal will mandate free and cheap medical care in public and private hospitals, clinics, and laboratories if implemented.
- Rajasthan would be the first state government to create and defend patients’ legal rights to equal healthcare treatment.
- The Bill also calls for the improvement of the public healthcare system.
Rajasthan Right to Health Bill
- Overview
- The right to health bill is part of the Rajasthan government’s effort to extend and strengthen the state’s medical services.
- The chief minister recently sanctioned Rs 117 crore to enhance facilities at the Mahila Chikitsalaya at Sanganeri Gate in Jaipur.
- By the Mukhyamantri Chiranjeevi Swasthya Bima Yojana, the state has also secured the health security of every family by providing free treatment up to Rs 10 lakh to the people.
- In addition, families enrolled in the scheme will receive accident insurance worth up to Rs 5 lakh.
- Furthermore, drugs and diagnostics for patients visiting government health facilities are free.
Right to Health
- About
- The freedom to control one’s health and body is one of the liberties (for example, sexual and reproductive rights).
- Also, to be free of interference (for example, free from torture and non-consensual medical treatment and experimentation).
- Entitlements include the right to a healthcare system that provides everyone with an equal opportunity to achieve the best possible level of health.
Features of this Right
- The right to an appropriate quality of life was addressed in the 1948 Universal Declaration of Human Rights as part of the right to health (article 25).
- It includes;
- The highest possible level of physical and mental health.
- Stillbirth and infant death rates should be reduced.
- Healthy Child development.
- Hygiene in the workplace and the environment.
- Epidemic, endemic, occupational, illness prevention, treatment, and control.
- In the event of illness, guarantee all medical services and treatment.
Significance
- Right-Based Healthcare Services
- People have the right to health, which obligates the government to act.
- Wide Access to Health Services
- It allows everyone to access services and guarantees that the quality of those services is high enough to improve the health of those who receive them.
- Reduce Out of Pocket Expenditure
- Protects people from the financial consequences of paying for health care out of their own pockets.
- Furthermore, it lowers the likelihood of people falling into poverty.
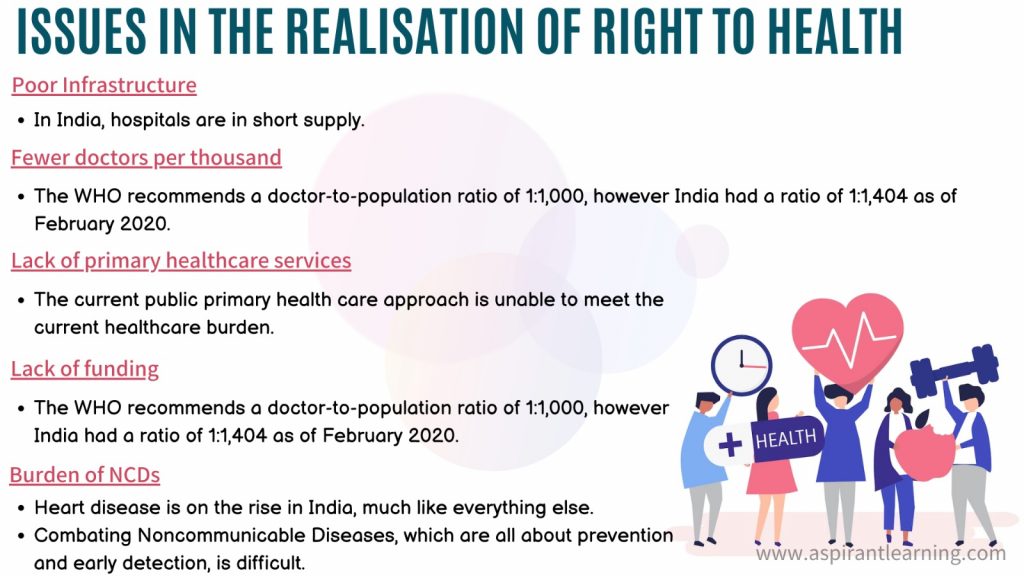
Challenges in the Health Sector
- Lack of Primary Healthcare Services
- Firstly, the country’s current public primary healthcare paradigm is limited in scope.
- Even though a well-functioning public primary health centre exists, only pregnancy care, limited daycare, and services related to national health programmes are available.
- Inadequate Funding
- In India, public health spending has been continuously low (about 1.3% of GDP).
- According to the OECD, India’s total out-of-pocket expenditure is approximately 2.3% of GDP.
- Sub-optimal Public Health System
- As a result, tackling Noncommunicable Diseases, which are all about prevention and early identification, is complicated.
- It reduces readiness and effective management for new and emerging dangers such as the Covid-19 pandemic.
Way Forward
- Universal health coverage
- All countries have agreed to provide universal health coverage (UHC) by 2030 as part of the SDGs.
- Increasing healthcare professionals in numbers
- India has handled the COVID-19 pandemic admirably.
- Yet, given the disease surge, India desperately needs more medical personnel and facilities.
- More funding
- According to the National Health Policy of 2017, public health funding should be increased to at least 2.5% of GDP.
- Use of technology
- Mobile apps, online consultations, e-pharmacies, and other tools are becoming more popular.
- Furthermore, all of these are welcome and should be taken advantage of.
Pic Courtesy: Indian Express
Content Source: The Hindu



