News Highlight
Students and researchers in resource-poor labs can use Foldscopes and glows copes with revealing more about the microscopic world.
Key Takeaway
- Foldscope, a handheld microscope built almost entirely of paper, was introduced in 2014 by Stanford University academics, and it takes 30 minutes to assemble and may capture photos of cells.
- Millions of individuals, mostly schoolchildren, have used Foldscopes to capture photographs of the microscopic world, and hundreds of scientific research have been undertaken with this equipment.
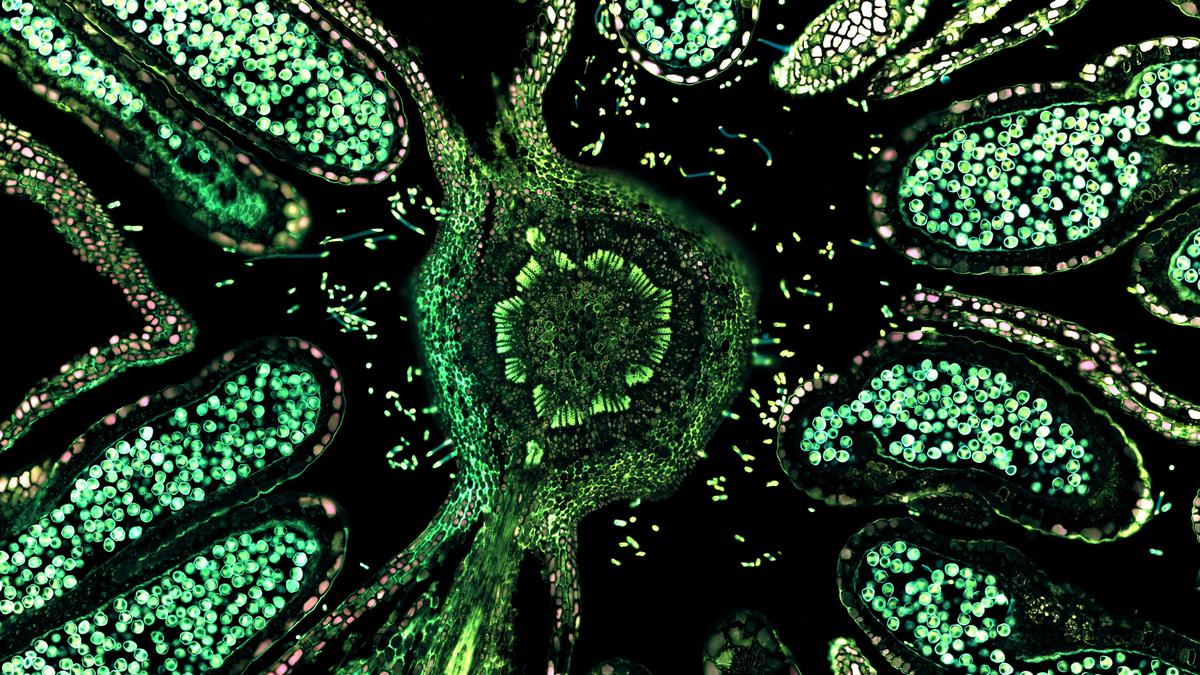
Fluorescence Microscope
- About
- An optical microscope that uses fluorescence and phosphorescence is called a fluorescence microscope.
- Moreover, reflection and absorption are used to investigate the characteristics of organic or inorganic substances.
- Fluorescence is the emission of light by a substance that has absorbed light or other forms of electromagnetic radiation.
- Phosphorescence is a sort of photoluminescence that is connected to fluorescence.
- A phosphorescent material, unlike fluorescence, does not immediately re-emit the energy it absorbs.
- August Köhler, Carl Reichert, and Heinrich Lehmann, among others, invented the fluorescence microscope in the early twentieth century.
- Working
- The excitation wavelength light is focused on the specimen through the objective lens.
- In addition, the objective directs the fluorescence emitted by the specimen to the detector.
- Because most excitation light is transmitted through the specimen, only reflected and emitted excitatory light reaches the objective.
- Principle
- Most cellular components are colourless and cannot be recognised under a microscope.
- The primary idea behind fluorescence microscopy is to colour the components.
- Fluorescent dyes, or fluorophores or fluorochromes, absorb excitation light at a specific wavelength and emit light at a longer wavelength after a brief delay.
- In addition, the time lag between absorption and emission is typically in the range of nanoseconds.
- The position of the fluorophores can then be shown by filtering the emission light from the excitation light.
Advantages of Fluorescence Microscope
- High sensitivity
- Firstly, low quantities of fluorescence can be detected using fluorescence microscopy.
- It is a sensitive technique to detect and visualise individual molecules or structures within a sample, and it can detect 50 molecules per cubic millimetre due to its increased sensitivity.
- High resolution
- Fluorescence microscopy may produce high-resolution images, allowing you to see minute structures and details within a sample.
- Non-destructive
- Fluorescence microscopy is a non-destructive method, which means it does not cause any harm to the sample being imaged.
- Furthermore, this enables the sample to be scanned several times or for additional studies on the same sample.
- Live-cell imaging
- It is used to investigate the dynamic behaviour seen in live-cell imaging.
- Use in different Fields
- Fluorescence microscopy has biological, biomedical, and material science applications.
- Furthermore, fluorescence microscopes’ unique capabilities enable the precise and detailed identification of cells and sub-microscopic cellular components.
- Protein Location
- It can pinpoint the location of a specific protein within a cell.
Disadvantages of Fluorescence Microscope
- Photobleaching
- When fluorescent dyes and proteins are exposed to the light required to stimulate the fluorescence, they might be bleached or destroyed.
- In addition, the fluorescence signal may decrease, reducing the time a sample may be analysed.
- Phototoxicity
- The light used to trigger fluorescence in a sample can be hazardous to living cells, leading them to be harmed or die, and can make studying living cells or tissues over long periods challenging.
- Limited multiple labelling
- Fluorescence microscopes are limited in visualising several fluorophores in a sample simultaneously.
- Furthermore, studying complex systems or processes involving several molecules or structures can be difficult.
- Resolution limits
- Although superresolution microscopes have considerably improved fluorescent microscopy resolution.
- There are still limitations to the level of detail that these devices can visualise.
Application of Fluorescence Microscope
- The fluorescence microscope has become indispensable in medical microbiology and microbial ecology.
- Immunofluorescence can recognise bacterial pathogens after being stained with fluorescent dyes or specially labelled with fluorescent antibodies.
- The Fluorescence microscope is used in ecological research to study microorganisms stained with Fluorochrome-label probes or Fluorochromes that bind certain call constituents.
- Localising specific proteins within the cell is another important application of fluorescent microscopy.
- Fluorescence microscopy has biological, biomedical, and material science applications.
- Fluorescence microscopes’ unique capabilities enable the precise and detailed identification of cells and sub-microscopic cellular components.
- Fluorescence microscopy is widely used in histochemistry research to detect unseen particles such as neurotransmitter amines.
- Furthermore, it is used in food chemistry to assess specific dietary components’ presence, structural structure, and spatial distribution.

Pic Courtesy: The Hindu
Content Source: The Hindu