News Highlights:
Turkey-Syria earthquake: On February 6, a significant earthquake that was felt in both Turkey and Syria killed more than 3,800 people and destroyed thousands of houses while rescuers dug with their own hands for survivors.
Key takeaway:
Three earthquakes with Richter scale magnitudes of 7.8, 7.6, and 6.0 struck distant areas such as Cyprus (456 km), Lebanon (874 km), Israel (1,381 km), and Egypt (1,411 km).
Earthquake Status
- The story so far:
- The tremors of the first quake were felt on February 6 around 4 a.m., with the epicentre located near the city of Gaziantep in south-central Turkey, which houses more than two million people.
- This population includes scores of Syrian refugees who fled the raging civil war after 2011.
- Nine hours later, two further earthquakes with magnitudes of 7.6 and 6.0 struck the region.
- As of Tuesday morning, this earthquake, the largest to hit the area in more than a century, had killed at least 3,800 people in Turkey and Syria.
- Damage Caused:
- According to the U.S. Geological Survey, the quake’s focus was 18 km deep.
- The epicentre was about 33 km from Gaziantep.
- The area has many buildings constructed of brittle concrete (which makes them prone to cracking, spalling, loss of strength, or steel corrosion), making them “extremely vulnerable to earthquake shaking.
- Nearly 900 buildings were reportedly destroyed in Turkey’s Gaziantep and Kahramanmaras provinces,
- The runway at Turkey’s Hatay Airport was torn open due to the earthquake’s magnitude.
- According to officials, the earthquake in Turkey has hit at least 10 cities, with more than 2,818 buildings suffering damage.
- The city’s most recognisable landmark, a mediaeval stone castle that is 2,200 years old and was utilised as an observation post during Roman times, is damaged, with its walls and watch towers crumbling.
- The renowned Yeni Mosque, built in the 13th century and one of Maltaya’s most notable landmarks, had collapsed.
- International aid:
- Many are still believed to be buried under the rubble, and more than 2,000 people may have been hurt.
- Turkey has issued a Level 4 alert requesting assistance from abroad; according to reports, the United States, European Union, Russia, and Azerbaijan have already sent assistance.
Earthquake:
- About:
- An earthquake, in simple words, is the shaking of the earth. It is a natural event. It is caused due to release of energy, which generates waves that travel in all directions.
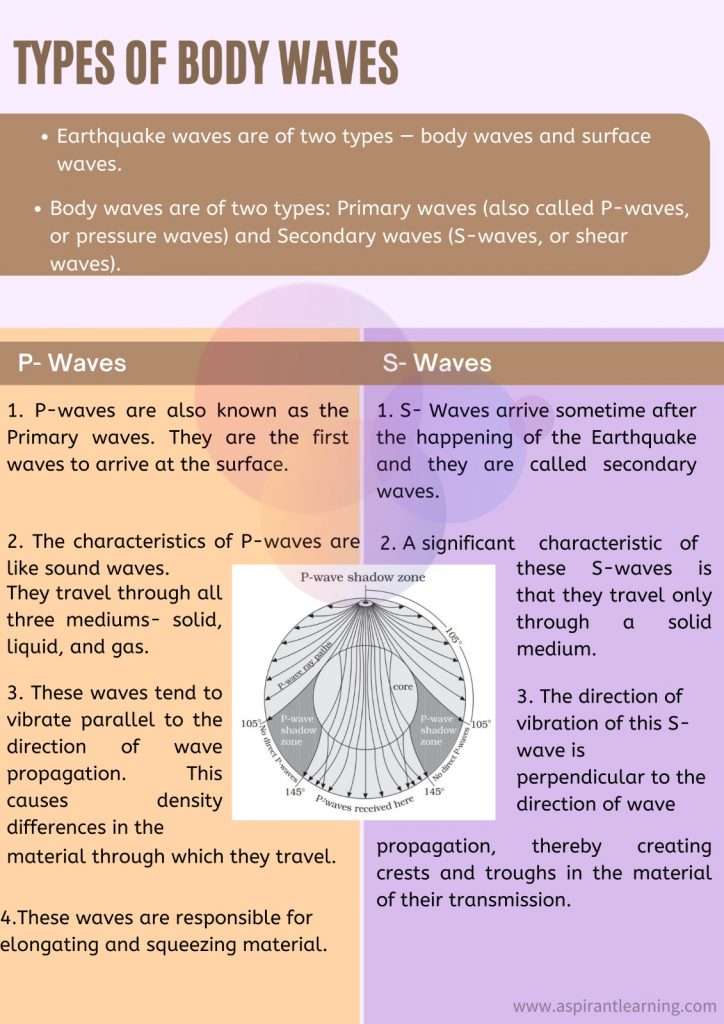
- The vibrations called seismic waves are generated from earthquakes that travel through the Earth and are recorded on instruments called seismographs.
- Types of Earthquakes:
- Tectonic earthquakes: The most common form of an earthquake is caused by the movement of loose, fragmented pieces of land on the earth’s crust, knowns as tectonic plates.
- Volcanic earthquake: The less prevalent than the tectonic variety, these earthquakes happen before or after the eruption of a volcano. It is caused when magma leaving the volcano is filled by rocks being pushed to the surface.
- Collapse earthquake: This earthquake occurs in underground mines. The leading cause is the pressure generated within the rocks.
- Explosion earthquakes: The occurrence of this type of earthquake is artificial. High-density explosion, such as nuclear explosions, is the primary cause.
- Causes of Earthquakes:
- It results from the earth’s tectonic motions.
- Waves that propagate in all directions are created when energy is released.
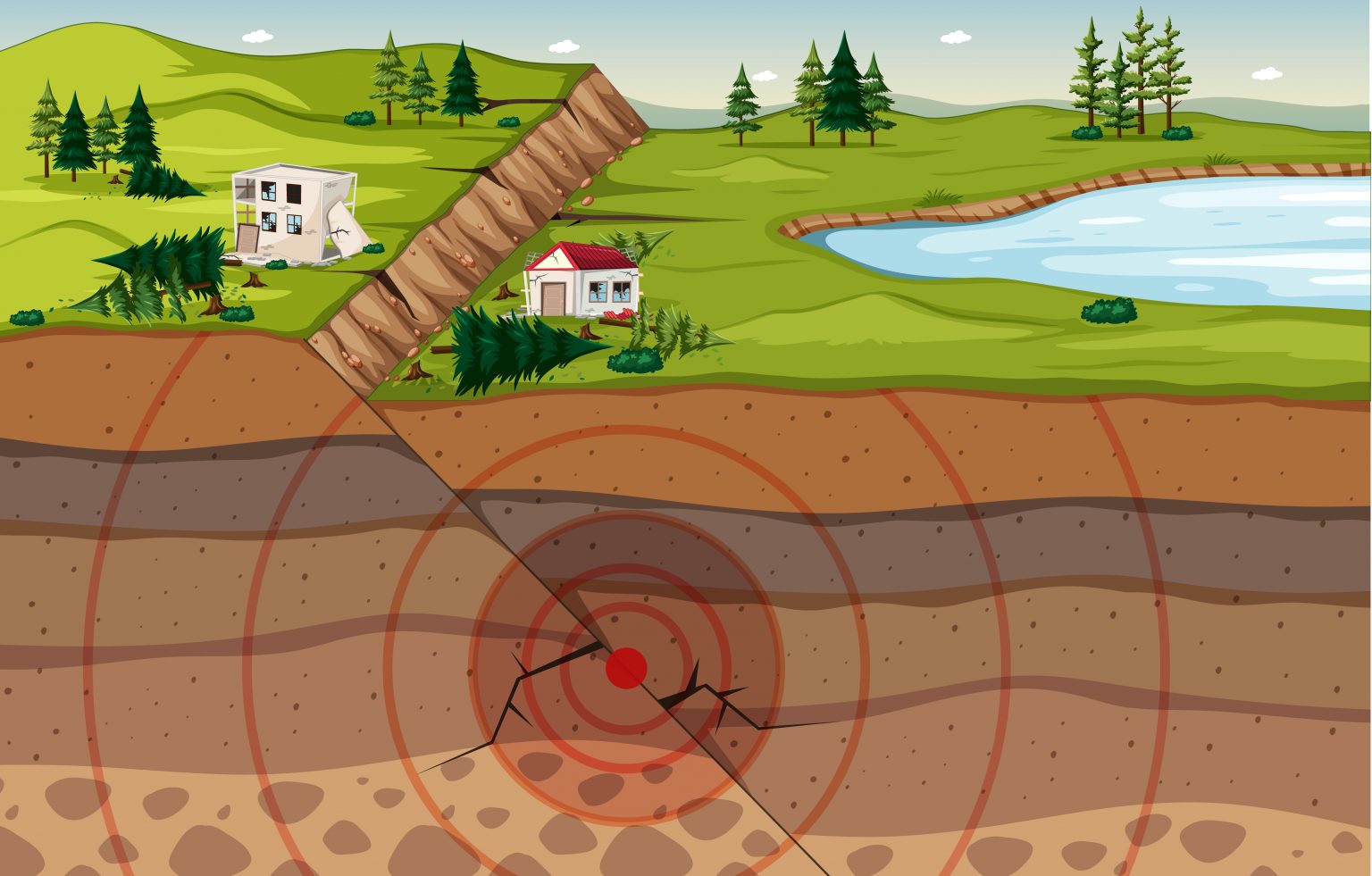
- The focus or hypocentre is the location where energy is released. It typically lies 60 kilometres below the surface.
- Energy is released as a result, and energy waves spread in all directions.
- The focus or hypocentre of an earthquake is the location where the energy is released.
- The epicentre is the location on Earth’s surface directly above the focus. It is the first location where waves are felt.
- Effects of an earthquake:
- Shaking of ground
- The disparity in ground settlement
- Natural disasters like Tsunami, landslides, mudslides, and avalanches
- Soil liquefaction
- Ground lurching and displacement
- Floods and fires
- Infrastructure collapse.
Pic Courtesy: Freepik
Content Source: The Hindu