News Highlights:
Several parts of Europe are witnessing an unprecedented winter heat wave. Large swathes of Europe, the U.K. and the U.S. are sweltering under extreme heat wave conditions.
Key Takeaway:
- Experts said temperatures increased 10 to 20 degrees Celsius above average, Calling it an “extreme event”.
- According to the report, at least seven countries recorded their hottest January weather ever because of the formation of a heat dome over the region.
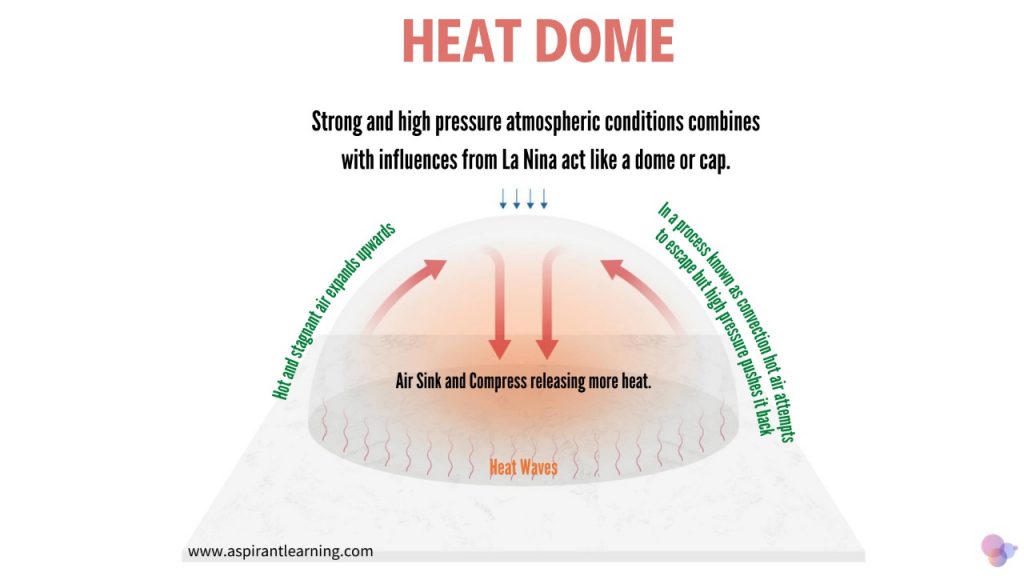
What is Heat Dome?
- About:
- It is a warm air mountain built into a wavy jet stream, with extreme undulations.
- As per the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), a heat dome occurs when the atmosphere traps hot ocean air like a lid or a cap.
- Cause of Heat dome:
- The phenomenon of Heat dome starts when there is a significant change (or gradient) in the ocean temperatures.
- In the convection process, the gradient causes more warm air, heated by the ocean surface, to rise over the ocean surface.
- The prevailing winds move the hot air east, and the northern shifts of the jet stream trap the air and move it toward the land, where it sinks and results in heatwaves.
- Jet streams are relatively narrow bands of strong wind in the upper levels of the atmosphere. The winds blow west to east in jet streams, but the flow often shifts to the north and south.
- This intense change in ocean temperature from the west to the east is the reason for the heat dome (HD).
heat domes and the jet stream:
- Relations:
- The heat dome’s formation is related to the behaviour of the jet stream — an area of fast-moving air high in the atmosphere.
- The jet stream is believed to have a wave-like pattern that keeps moving from north to south and then north again.
- When these waves get more extensive and elongated, they move slowly and sometimes become stationary.
- This is when a high-pressure system gets stuck and leads to the occurrence of a heat dome.
Heat Waves:
- About:
- It is a period of unusually hot weather that lasts more than two days.
- Heatwaves can occur with or without high humidity and can potentially cover a large area, exposing many people to hazardous heat.
- Criteria:
- The IMD says a heatwave is considered when the maximum temperature of a station touches at least 40 degrees Celsius or more for plains, 37 degrees Celsius or more for coastal regions and at least 30 degrees Celsius or more for hilly regions.
- Heatwave is declared when the departure from average temperature is by 4.5 to 6.4 degrees Celsius, and a severe heatwave is when the departure from usual is more than 6.4 degrees Celsius.
- For plains, based on actual maximum temperature, IMD considers heat waves when the actual maximum temperature is more than 45 degrees Celsius and severe heat waves when it is more than 47 degrees Celsius.
- This apart, if the locality records over 45 degrees and 47 degrees on any given day, then the IMD declares heatwave and severe heatwave.
Impact of Climate Change due to Heat dome:
- Although heat domes are likely to have always existed, researchers say that climate change may make them more intense and more prolonged.
- They suggest with the rising temperatures, it is expected that the jet streams will become wavier and will have more significant deviations, causing more frequent extreme heat events.
Effects of Extreme Heat Conditions:
- Health Risk:
- One of the most significant health risks in a heatwave such as this one is heatstroke.
- Heatstroke can lead to many severe problems, including damage to the brain, heart, muscles and internal organs.
- Older people are more susceptible to heatstroke, as the body’s ability to regulate heat deteriorates with age.
- Forest:
- Hotter weather saps moisture from vegetation, turning it into dry fuel that helps fires to spread.
- Results In Forest Fire.
- Agriculture:
- It can also severely impact agriculture.
- It either causes vegetables to wilt and die or encourages the spread of plant diseases.
- It can result in Forest fires.
- Ecological:
- The severe heat waves reduce forest cover.
- Heat waves result in the deterioration of Fauna and Flora.
- Infrastructure:
- It affects infrastructure, too, by straining power grids and causing blackouts.
- It can ground planes, melt roads and cause the inside of vehicles to overheat to dangerous levels.
Pic Courtesy: Freepik
Content Source: The Indian Express



