News Highlight
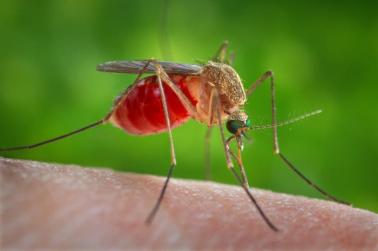
The New York City Health Department announced that the West Nile virus has been detected in two people as well as in a “record number” of infected mosquitoes throughout the city.
Key Takeaway
- A total of 54 cases and four deaths have been reported throughout the country this year.
- Higher than average temperatures are a factor in the ‘record number’ of West Nile virus-infected mosquitoes in New York City.
The West Nile virus (WNV)
- The West Nile Virus (WNV) is a member of the flavivirus genus and belongs to the Japanese encephalitis antigenic complex of the family Flaviviridae.
- It was first identified in birds in the Nile delta region in 1953.
- It can cause a fatal neurological disease in humans.
- Outbreaks:
- It was first isolated in the West Nile district of Uganda in 1937.
- Human infections attributable to WNV have been reported in many countries in the world for over 50 years.
- Transmission:
- Human infection is most often the result of bites from infected mosquitoes.
- Mosquitoes become infected when they feed on infected birds, which circulate the virus in their blood for a few days.
- A very small proportion of human infections have occurred through organ transplants, blood transfusions and breast milk.
- To date, no human-to-human transmission of WNV through casual contact has been documented.
- Signs and symptoms:
- Infection with WNV is asymptomatic (no symptoms) in around 80% of infected people.
- About 20% of people who become infected with WNV will develop West Nile fever.
- Symptoms include fever, headache, tiredness, and body aches, nausea; vomiting.
- The incubation period is usually 3 to 14 days.
- Diagnosis:
- The West Nile virus can be diagnosed by a number of different tests:
- IgG antibody seroconversion (or significant increase in antibody titers) in two serial specimens collected at a one-week interval by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA)
- IgM antibody capture enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA)
- Neutralisation assays
- Viral detection by reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) assay.
- Virus isolation by cell culture.
- Treatment and vaccine:
- Treatment is supportive for patients with neuro-invasive West Nile virus, often involving hospitalisation, intravenous fluids, respiratory support, and prevention of secondary infections.
- No vaccine is available for humans.
- Vectors and animal hosts:
- The WN virus is maintained in nature in a mosquito-bird-mosquito transmission cycle.
- Mosquitoes of the genus Culex are generally considered the principal vectors of WNV, in particular Cx. pipiens.
- Birds are the reservoir hosts of WNV.
Content Source: The Hindu