News Highlights
On June 28, NATO Secretary announced the signing of a MoU between Turkey, Finland and Sweden which has led to Turkey vocalizing its support for the inclusion of both the nations in NATO.
Background
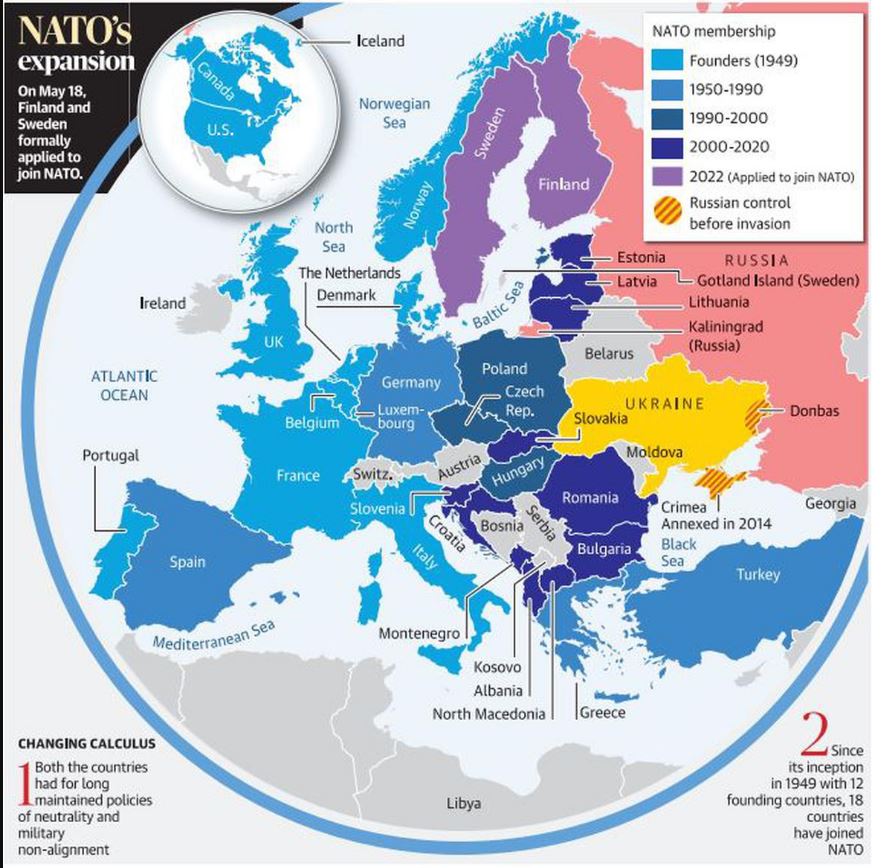
- Following Russia’s invasion of Ukraine, Sweden and Finland abandoned their long-held nonaligned status and applied to join NATO.
- Initially Turkey, a NATO member since 1952 blocked the move, insisting that the Nordic pair change their stance on Kurdish insurgent groups that Turkey considers terrorists.
- Later NATO announced the signing of a memorandum of understanding (MoU) between Turkey, Finland and Sweden in a trilateral meeting held in Spain
- Turkey agreed to support inviting the two Nordic countries into the military alliance, after receiving pledges from Finland and Sweden addressing its security concerns, including restrictions on Kurdish groups that Turkey considers terrorists, and avoiding arms embargoes.
What does MoU say ?
- The key provisions of the MoU include
- A joint commitment between Turkey, Finland, and Sweden to counter terrorism
- Using a bilateral legal framework to address the pending extradition of terror suspects, as well as investigating and
- Blockading any financing and recruitment activities of the Kurdistan Workers’ Party (PKK) and all other terrorist organisations.
Other commitments from Sweden and Finland
- Finland and Sweden pledged that “their respective national regulatory frameworks for arms exports will implement new obligations for allies.”
- Both countries pledged to stand against disinformation and to fully engage with the EU’s CSDP (Common Security and Defense Policy) and Turkey’s participation in the PESCO (Permanent Structured Cooperation) program on military mobility.
Why did Turkey withdraw its opposition?
- Turkey, agreed to withdraw its opposition for the following reasons.
- Finland and Sweden should promise to address counter terrorism provisions within their countries.
- Finland has committed to modify its criminal code, and Sweden has assured to implement the new “Terrorist Offenses Act” from July 1.
- Turkey had raised concerns about Finland and Sweden being home to Kurdish activists and militant organizations.
- Finland and Sweden have now agreed to execute the pending “deportations or extraditions” of listed ‘terror’ suspects made by Turkey.
- Lifting the Arms embargo.
- There has been no clear definition about the category of weapons, but Finland and Sweden will remove the arms embargo against Turkey.
- Finland and Sweden should promise to address counter terrorism provisions within their countries.
Why have Finland and Sweden agreed to address Turkey’s concerns?
- Russia’s security threat emerges in Finland and Sweden’s national capitals, as Russia’s military aggression against Ukraine continues.
- The fear of their own national security has pushed both nations to join NATO which in turn has made them agree to Turkey’s conditions.
How does this affect Russia?
- Increased NATO presence in Russia’s neighborhood
- Since 1948, Finland, Sweden and Russia have maintained economic cooperation, but the relations always remained strained due to the Cold War and Finland’s neutrality principle.
- If Sweden and Finland join NATO, it means an enlarged presence of NATO around the west and north of Russia.
- This would go against the very objective of Moscow interfering in Ukraine that is maintaining Russian influence in its immediate neighborhood
- Questions Russia’s Arctic interests.
- Both Sweden and Finland are part of the Arctic States; Russia currently holds the Arctic Council chair and will remain the chair until 2023.
Significance for NATO?
- Strengthening the alliance
- Both Finland and Sweden which have followed the nonalignment principle have broken and decided to join NATO.
- This does not only mean guarantee of security against Russia but it also gives NATO the power to engage.
- Creates strategic ground to counter Russia
- The addition of more allies means a steady expansion of NATO towards the East
- It will now be able to exercise its military operations both on land and in the Baltic Sea, where Russia holds a strategic position.
- NATO will now also be able to position its weapon systems — further its combat formation and plan its attack techniques to power up deterrence and defense.
- Initiates the way to normalizing the relation
- In 1997, NATO initiated the reconciliation in order to build bridges with Russia.
- However, with Russia annexing the Crimean Peninsula in 2014 and launching a war in Ukraine, NATO’s reconciliation efforts came to an end.
- By NATO encircling Russia from the West, Russia may consider the option to meet at a later stage.
- Secured EuroAtlantic
- NATO presence in the region will securitise and safeguard the Baltic states, Estonia, Latvia and Lithuania, which were earlier at risk due to their close proximity to Russia and Russian attacks.
- This will not only help Ukraine win the war but will also enable NATO to bring in advanced weapons such as fifth generation aircraft, technological weapon systems and strong political institutions across the allied countries.
About North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO)
- North Atlantic Treaty Organization is an intergovernmental military alliance based on the North Atlantic Treaty which was signed on 4 April 1949.
- Aim: To constitutes a system of collective security, whereby its independent member states agree to mutual defence in response to an attack by any external party.
- Head quarters: Brussels, Belgium
- NATO Member Countries
- 12 founding members of the Alliance – Belgium, Canada, Denmark, France, Italy, Iceland, Luxembourg, the Netherlands, Norway, Portugal, the UK and the US.
- The other members who later joined: Greece, Turkey, Germany, Spain, the Czech Republic, Hungary, Poland, Bulgaria, Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania, Romania, Slovakia, Slovenia, Albania, Croatia, Montenegro and North Macedonia.
- North Macedonia is the latest to join the grouping in the year 2020.
- Important events in the Emergence of NATO
- The founding members of NATO signed the North Atlantic Treaty on April 4, 1949, NATO’s primary purpose was to defend member nations from threats by communist countries.
- During the Cold War, NATO’s mission expanded to prevent nuclear war.
- After West Germany joined NATO, the communist countries formed the Warsaw Pact alliance
- In response, NATO adopted the “Massive Retaliation” policy. It promised to use nuclear weapons if members of the Pact attacked
- After the USSR dissolved in the early 1990s, NATO’s relationship with Russia thawed.
- In 1995 NATO engages in its first major crisis-management operation in Bosnia and Herzegovina
- In 1997, they signed the NATO-Russia Founding Act to build bilateral cooperation.
- In 2002, they formed the NATO-Russia Council to partner on shared security issues.
- NATO participates in three alliances that expand its influence beyond its 30 member countries
Pic Courtesy: The Hindu
Content Source: The Hindu



