News Highlights
Madhya Pradesh is planning to make sand mining legal around Chambal Wildlife Sanctuary legal. Opening a legal window to meet local requirements should minimize the pressure of illegal mining.
Focus Points
- Aim of the move –
- To minimize the cost of Madhya Pradesh forest department from devoting too much time , resources and efforts in fighting illegal in Chambal Wildlife Sanctuary, Madhya Pradesh.
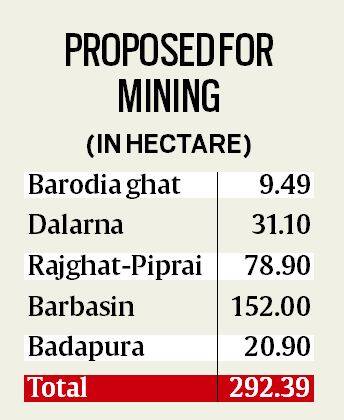
- As per the government has proposed to open 292 hectares for mining in five stretches on Chambal and its tributaries Parvati rivers.
- Sand mining has been banned in the sanctuary since 2006.
- State Report to Centre
- In a December 2021 proposal submitted to Union Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate and Change (MoEF &CC), the state said the opening up the five stretches would minimise the conflict with illegal miners , gain local supports and fetch revenue from royalty, one fourth for protection of which used for protection measures.
- The proposal also makes the contractors legal queries which will check the illegal mining near to sanctuary land four times their leased areas , failing to do so leases will be terminated.
National Chambal Wildlife Sanctuary
- Location – Madhya Pradesh , Uttar Pradesh , Rajasthan
- Year of Establishment – 1979
- Aim of Establishment – Established under the crocodile conservation project to protect Indian Gharials as a riverine sanctuary
- The National Chambal Sanctuary is a proposed Ramsar site and is designated as an important bird area (IBA).
- The Sanctuary’s biodiversity includes the marsh crocodile or mugger, seven species of freshwater turtles, Ganges river dolphins, and 78 species of wetland birds, in addition to the gharial and smooth-coated otter.
Chambal River
- Origin – Singar Chouri peak in the northern slopes of the Vindhya mountains (Madhya Pradesh)
- Mouth – Yamuna River
- Length – 960 km
- Borders
- It is a rainfed river and its basin is bounded by the Vindhyan mountain ranges and the Aravallis.
- Draining Region
- The Chambal and its tributaries go across northwestern Madhya Pradesh’s Malwa region.
- Tributaries
- Banas, Kali, Sindh, Parbati.
- Main Power Projects
- Gandhi Sagar Dam, Rana Pratap Sagar Dam, Jawahar Sagar Dam, and Kota Barrage.
Pic Courtesy : Indian Express
Content Source : Indian Express



