News Highlights
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) is scrutinizing the neobank business model, in which fintech’s connect to a traditional bank’s network and provide customer-facing banking services.
Focus Points
- The issue is that the digital model business can grow rapidly and could grow to be bigger than the underlying bank in terms of customers.
- There are half a dozen of neobanks in India that specifically target the customers that are not visiting the respective bank branches.
Other Suggestion of RBI Working Groups
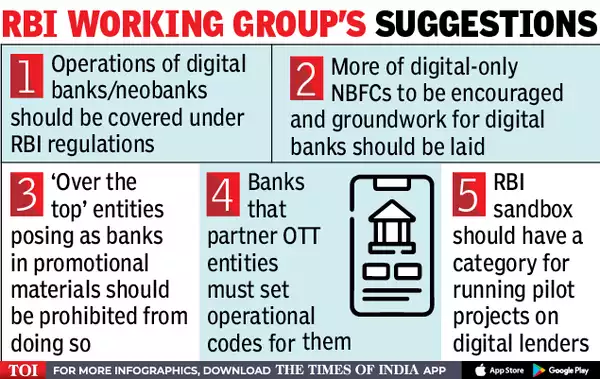
What is Neobanks?
- Neobanks are financial institutions that give customers a cheaper alternative to traditional banks.
- It is a type of digital bank that does not have any physical locations.
- Does not require you to be physically present at a specific location and they are less expensive in nature
- They use artificial intelligence and technology to provide tailored services to clients while lowering operating expenses.
- What do they provide?
- Provides digital and mobile-first services like payments, debit cards, money transfers, lending, and more.
- They bridge the gap between the services that traditional banks offer and the evolving expectations of new-age customers.
- These companies don’t have their own bank licenses in India, hence they rely on bank partners to provide licensed services.
- That’s because the RBI doesn’t allow banks to be 100% digital yet.
- The RBI has stated that banks’ physical presence should be prioritized, and that digital banking service providers should have some physical presence as well.
- Examples of Neobanks – FI Money, and Kotak811
Different Operating Models of Neobanks
- Non-licensed FinTech – Non-licensed FinTech companies that work with traditional banks to create a mobile/web platform and wrapper around their partners’ products.
- Traditional banks – Traditional financial institutions that are launching digital initiatives.
- Licensed neobanks – Neobanks with a license.
Differences Between Traditional Banks and Neobanks
- Customers’ trust and funding
- Traditional banks have a number of advantages versus neobanks, including funding and, most significantly, the trust of their consumers.
- Legacy systems, on the other hand, are weighting companies down, making it impossible for them to adapt to the changing needs of a tech-savvy youth.
- Innovation
- While neobanks lack the money and client base to defeat traditional banks, they do have one unique weapon: innovation.
- They may introduce new products and form partnerships to better serve their consumers far faster than traditional banks.
- Underserved by traditional banks
- Retail clients, as well as small and medium businesses, are served by neobanks, which are underserved by traditional banks.
- They use the mobile-first concept to set themselves apart by introducing cutting-edge products and providing exceptional customer service.
- Venture capital and private equity investors
- Investors in venture capital and private equity have been paying close attention to the market prospects for such banks and are becoming increasingly interested in them.
- Smartphone penetration
- India has a 54 percent Smartphone penetration rate in 2020, which is expected to rise to 96 percent by 2040.
- Financial inclusion levels have yet to improve, despite the fact that 80 percent of the population has access to at least one bank account.
Advantages of Neobanks
- Less Cost
- They can keep their costs low because of less rules and the absence of credit risk. The majority of products are low-cost, with no monthly costs.
- Convenience
- Customers can access the bulk (if not all) of their banking services through an app provided by these banks.
- Speed
- Customers can rapidly open accounts and have requests processed by Neobanks. Those that provide loans may use novel credit evaluation procedures instead of the traditional time-consuming application processes.
- Transparency
- Neobanks try to be transparent, providing real-time warnings and explanations of any fees or penalties imposed by customers.
Issues with Neobanks
- Meeting the needs of a specific market segment
- The key to their success is meeting the needs of a certain market niche, as well as implementing the appropriate technology, corporate strategy, and work culture.
- Regulatory Issues
- Because the RBI has yet to recognise neobanks as such, clients may be without legal redress or a specified mechanism in the event of a problem.
- Impersonal
- Since neobanks don’t have a physical branch, customers don’t have access to in-person assistance.
- Few Services
- Neobanks generally offer fewer services than traditional banks.
Pic Courtesy : Times of India
Content Source : Times of India



