News Highlights
Foreign ministers of the BRICS grouping expressed concern at the impact of the conflict in Ukraine on global energy and food security and backed talks between Moscow and Kyiv.
Areas of Focus
- Meeting that discussed ways to further intra-BRICS cooperation in politics and security, economy and finance, and people-to-people and cultural exchanges
- The meeting, which was chaired by Chinese foreign minister Wang Yi under the rotating presidency of Brics, discussed the situation in Ukraine and “supported talks between Russia and Ukraine.
- Meeting also condemned global terrorism.
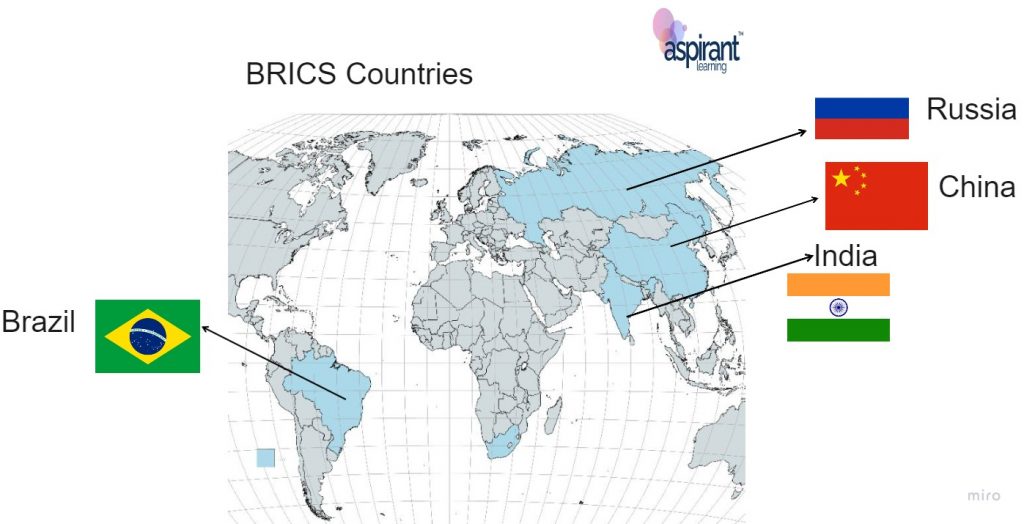
What is BRICS?
- BRICS grouping includes world’s leading emerging economies, namely
- Structure of BRICS
- It is not a formal organisation; rather, it is an annual summit between the leaders of five countries.
- According to the formula B-R-I-C-S, the chairmanship of the forum is rotated annually among the members.
- Over the last decade, BRICS cooperation has grown to include an annual programme of over 100 sectoral meetings.
- Timeline of BRICS

- Objectives of BRICS
- For more sustainable, equitable, and mutually beneficial development, the grouping aspire to deepen, broaden, and accelerate collaboration within the grouping and among individual nations.
- To guarantee that interactions are established on the respective country’s economic strengths and to prevent competition whenever possible, grouping takes into account each member’s growth, development, and poverty objectives.
- BRICS is establishing itself as a new and promising political-diplomatic body with a wide range of goals that extend far beyond the basic goal of overhauling global financial institutions.
Areas of Cooperation in BRICS
- Economic Cooperation
- Trade and investment flows between BRICS countries are quickly increasing, as are economic cooperation efforts in a variety of industries.
- Economic and trade cooperation, innovation cooperation, customs cooperation, strategic cooperation between the BRICS Business Council, contingent reserve agreement, and the New Development Bank all have agreements in place.
- Political and Security Cooperation
- The goal of BRICS member countries’ political and security cooperation is to achieve peace, security, development, and collaboration in order to create a more equitable and fair world.
- It provides possibilities for policy advice and best practice exchanges on domestic and regional concerns, as well as pushing the restructuring of the global political infrastructure to make it more balanced, based on multilateralism.
- South Africa’s foreign policy initiatives, particularly the promotion of the African Agenda and South-South Cooperation, are driven by the grouping.
- People – People Cooperation
- The need to strengthen People-to-People interactions and create closer collaboration in the areas of culture, sport, education, cinema, and youth has been recognised by BRICS members.
- In the spirit of openness, inclusion, diversity, and mutual learning, people-to-people interactions aim to establish new connections, develop relations, and mutual understanding between BRICS peoples.
- The Young Diplomats Forum, Parliamentarian Forum, Trade Union Forum and Media Forum are examples of people-to-people encounters.
Significant Steps in BRICS Growth
- New Development Bank
- The member countries agreed to construct a new global financial institution during their fifth summit in Durban, South Africa, in 2013, which became the New Development Bank in 2015.
- It was founded in Shanghai with an initial capital of $50 billion, which was later increased to $100 billion.
- The bank is now seen as a competitor to the World Bank, with its principal focus on lending for various development initiatives in member and developing nations.
- In just five years, the NDB, the grouping’s signature achievement, has 44 projects and has lent $12.4 billion.
- NDB has regional offices in South Africa and Brazil, with Russia and India following suit in 2020.
- Johannesburg Declaration, 2018 – Mutual respect, sovereign equality, democracy, inclusion, and greater collaboration were all reiterated by the leaders.
- New Industrial Revolution – The leaders praised the formation of the BRICS New Industrial Revolution Partnership (PartNIR).
- BRICS Plus
- At the Xiamen summit last year, China launched the “BRICS Plus” model by inviting a few countries from various regions.
- The specific function of the “BRICS Plus” countries will take time to develop, but one immediate benefit is the enormous networking opportunities it affords for leaders.
- Brasilia Outcome
- The grouping reported 30 new accomplishments, initiatives, and papers under Brazil’s chairmanship.
- It promotes and supports multilateralism, the United Nations’ primary position in international affairs, and the rule of law.
- Financial Settings
- The BRICS states are planning to establish a Local Currency Bond Fund after a successful Contingent Reserve Arrangement.
- Contingent Reserve Agreement
- The group has also committed to a Contingent Reserve Agreement to protect members against immediate economic shocks.
- The pact protects member nations from global liquidity pressure because all members are developing economies that are vulnerable to greater economic volatility in the current globalized environment, and it is seen as a competitor to the International Monetary Fund.
Relevance of BRICS in Today’s World
- Check on Western Dominance
- The BRICS are a group of countries with a combined population of around 3.6 billion people, accounting for roughly 40% of the world’s population.
- In addition, the combined economies of the group members total roughly 17 trillion in nominal terms, or 22 percent of the global economy in the current environment.
- When the group is viewed as a competitor to the western-dominated World Bank and IMF, its importance grows.
- Financial Viewpoint
- The global financial crisis of 2008 created structural imbalances, and new challenges to the global economy such as trade wars and unilateral economic penalties have yet to be resolved.
- The BRICS’ expanding economic contribution and the growing importance of economic linkages between the BRICS and other Emerging Market and Developing Countries (EMDCs) provide an opportunity for new initiatives to better support sustainable and inclusive growth and development.
- Platform for Global Issues
- BRICS brings India, Brazil, Russia, China, and South Africa together to actively engage on global concerns.
- For example, the global financial and security situation, counter-terrorism, climate change, sustainable development, multilateral system reform, WTO reform, and international governance institutions, and ways to promote intra-BRICS cooperation in science and technology, trade, health, ICT, and people-to-people exchanges.
- Counter Terrorism
- The BRICS Counter-Terrorism Working Group has formed subgroups to address various areas of terrorism.
- BRICS has emerged as a prominent player in a world that is peaceful, affluent, and multipolar.
- BRICS leaders have backed India’s stance on counter-terrorism, stating that terrorism in any form or manifestation is unacceptable.
- Poverty Reduction
- The BRICS have made a significant contribution to global poverty reduction.
- Continued BRICS growth is critical for poverty reduction and the lowering of global disparities.
Why is BRICS vital for India?
- Geo-Politics
- Today’s global geopolitics resembles a tug of war, and India is caught in the centre of it. This has made it difficult for India to strike a balance between its strategic interests and those of the United States and the Russia-China axis.
- As a result, India can use the BRICS platform to counterbalance the Russia-China axis.
- Global Economy
- BRICS countries had a common goal of overhauling the international financial and monetary system, as well as a strong desire to create a more just and balanced international order.
- To this purpose, the BRICS countries play a significant role in the G20, influencing global economic policies and promoting financial stability.
- Terrorism
- Pursue member countries against global terrorism and protect security interests.
- Way to Global Platforms
- India is pursuing membership in the United Nations Security Council (UNSC) and the Nuclear Supplier Group (NSG) (NSG).
- China is a key impediment to achieving such aims. As a result, BRICS offers an opportunity to engage actively with China and settle mutual disputes. It also aids in the recruitment of other partner countries.
Recent Issues within BRICS
- Security Viewpoint
- Russia’s Ukraine invasion and Europe reaction
- Chinese aggression in the South China Sea , Indian borders.
- Economic Viewpoint
- Rise of other economies like Next 11 which include Indonesia, Mexico and Turkey
- China’s economic clout like the Belt and Road Initiative in 2017 and India , Russia not joining shows different interests .
- South Africa’s debt-laden economy and the negative current account
- Even before Covid-19, India’s economic decline was a source of concern, and government programmes like “Atma Nirbhar” were interpreted as an attempt to turn inward.
Common Challenges
- Heterogeneity: Critics argue that the BRICS nations’ heterogeneity (variable/different character of countries) and diverse interests pose a threat to the grouping’s existence.
- China-centric: Because all of the BRICS countries trade with China more than they do with each other, it is viewed as a platform to promote China’s interests. For other partner countries, balancing the trade imbalance with China is a big task.
- Global Governance Model: In the face of global slowdown, trade wars, and protectionism, the BRICS face a fundamental task in developing a new global governance model that is inclusive and constructive rather than unipolar.
Way Forward
- BRICS is a vital form of grouping to the world and individual country perspective to act as a global economic growth engine.
- It is also vital to check the global clout of western powers in international institutions.
- In Indian viewpoint it can help India for rapid economic growth and provide a platform to solve mutual bilateral issues.
Content Source : Hindustan Times



