News Highlights
- Prime Minister Narendra Modi will launch the construction of the India International Centre for Buddhist Culture and Heritage during a day-long visit to Lumbini in Nepal and offer prayers at Mayadevi temple.
- The visit will coincide with the celebrations to mark the Buddha Jayanti.
India International Centre for Buddhist Culture and Heritage
- The work on the centre will be undertaken by the International Buddhist Confederation (IBC).
- International Buddhist Confederation (IBC), is a “grantee body” under the Ministry of Culture.
- The International Buddhist Confederation was registered on November 2, 2012
- It is aimed at propagating and preserving the teachings and heritage of the Buddha across the world, and especially in India’s immediate neighbourhood.
Analyse India – Nepal Relation
- Nepal is considered an immediate Himalayan neighbour that shares common culture that include the birthplace of Buddha and mythical birthplace of Hindu goddess Seetha.
- Nepal borders five Indian states — Sikkim, West Bengal, Bihar, Uttar Pradesh, and Uttarakhand – on the south and the Tibet autonomous territory of the People’s Republic of China on the north.
- During the modern period of India – Nepal relation which started with both countries signing Friendship Treaty in 1950.
Provisions of Friendship Treaty, 1950
- Nepal citizens enjoy almost the same facilities as part of the treaty is signed with compared to Indians in case of opportunities available.
- But in today’s world the growing nationalism developing within Nepal and Maoist groups in Nepal opposing India’s intervention as part of this treaty.
Areas of Cooperation India – Nepal Relation
- Political Relation
- India and Nepal established India – Nepal Joint Commission
- Joint operations during disasters like Kathmandu earthquake( 2015) by using National Disaster Relief Force of India
- Regular bilateral visits
- Sharing common platforms like United Nations , BIMSTEC , SAARC

- Economic Relations – Areas of economic relation are
- Trade and Investment
- India is Nepal’s main trading partner and source of foreign investment, as well as providing transit for nearly all of Nepal’s trade with other nations. To improve relations, more trade is required.
- India provides Line of Credit to Nepal for development projects.
- Since 1996, Nepal’s exports to India have grown more than eleven times and bilateral trade more than seven times; the bilateral trade that was 29.8% of total external trade of Nepal in 1995-96 has reached 66% in 2012-13.
- Main items of exports from India to Nepal are petroleum products, vehicles and spare parts, mild-steel billets, machinery and parts, medicines, hot and cold rolled sheets, wires, rods, coils, bars, electrical equipment, cement, threads and chemicals.
- Main items of exports from Nepal to India are polyester yarn, textiles, jute goods, threads, zinc sheet, juice, cardamom, wire, pipe, copper wire rod.
- Infrastructure and Connectivity
- India assists Nepal with development, with a focus on building infrastructure at the local level.
- A Memorandum of Understanding was signed on the Raxaul-Kathmandu railway line. Inland waterway connectivity is also a priority for both countries. India should keep up the good work.
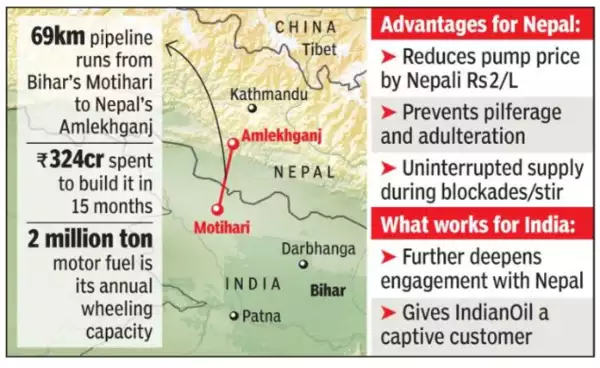
- In September 2019, inaugurated the Motihari-Amlekhgunj petroleum pipeline, first of its kind in South Asia.
- Trade and Investment
- Water Diplomacy
- In 2008, a three-tier system was developed to discuss all bilateral matters connected to water resources and hydropower cooperation.
- Nepal’s geography and numerous fast-flowing rivers make it excellent for hydroelectric power development.
- For example – On the Arun River in the Sankhuwasabha District of Province 1, East Nepal, the Arun-III hydroelectric facility is being built. With a 900MW power producing capacity, it is an export-oriented project.
- Defence Relation
- The Gorkha Regiments of the Indian Army are largely recruited from Nepal’s highland districts. Since 1950, India and Nepal have conferred the honorary rank of General on each other’s army chiefs.
- Joint defence exercises like Surya Kiran
- Capacity building programme for Nepal Army.
- Cultural Relations
- India and Nepal have common cultural relations like Buddhism and Hinduism.
- India provides educational scholarships to Nepali students.
- India and Nepal have high people to people contact through open connectivity.
- Indian culture center in Nepal.
- Nepal – Bharat Library.

Issues in India – Nepal Relation
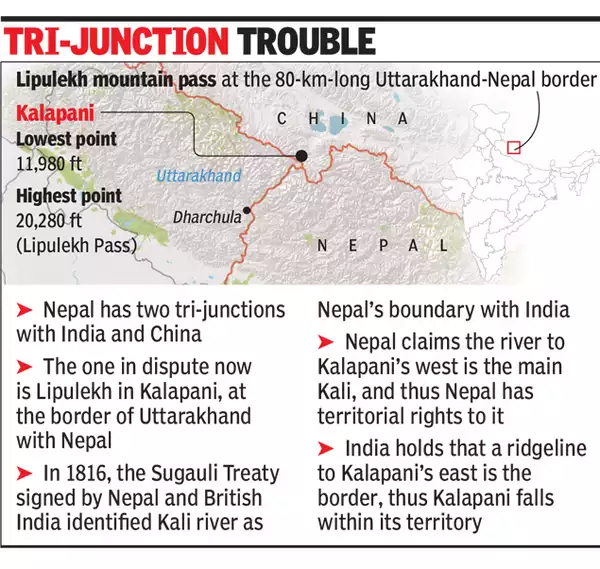
- Territorial Dispute
- The border between Nepal and India has some contentious issues, notably the two major regions of contention at Susta and Kalapani (India-China-Nepal tri-junction). Countries agreed to begin talks at the level of foreign secretaries to settle the issue, but only one meeting took place in 2015.
- Threat to India’s Internal Security
- The open border between India and Nepal encourages illicit migration and human trafficking, posing a security danger to India. Maoists, terrorists, and drug traffickers utilize the Indo-Nepal border as a launch pad.
- Spillover Effect of Nepal’s New Constitution
- In Nepal, a new constitution was adopted in 2015.
- It provided the governing hill tribes great political privileges while discriminating against populations residing in the plains, notably Madhesis.
- It also made it difficult for Madhesis to get citizenship. This has become a difficult issue between India and Nepal, which has resulted in an economic embargo by India, which has included gas supply, gasoline, and other essentials.
- Big Brother Syndrome
- In Nepal, there is a common belief that India does not respect the country’s sovereignty and frequently interferes in Nepal’s internal affairs. India has been portrayed as the region’s big brother.
- Nepal’s China Tilt
- In the coming years, China aims to expand the Tibet railway across the border to Kathmandu. Nepal and China inked a framework agreement for the Belt and Road Initiative (BRI).
Way Forward
- India should counter Chinese hard power by projecting soft power.
- India should boost integrated check posts to avoid issues like smuggling.
- Boost timely bilateral visits.
- Timely completion of India’s projects in Nepal and enhance trust between both parties.
Pic Courtesy: Times of India , The Economic Times
Content Source : New Indian Express



