Key Takeaways
- As part of coal mining in Odisha the Union Government owned Singareni Collieries Company Limited (SCCL) is going to fell 1 lakh trees.
- They aim to mine coal at the Naini mine in Chhendipada tehsil of the district.
- The total requirement of land for the project is 912.799 hectares, of which 643.095 hectares is reserve forestland and 140.18 hectares is village forestland.
- The SCCL is waiting for environment and forest clearance before diverting 783.275 hectares of forestland for the coal field, which is in the south-eastern corner of the lower Gondwana basin within the Mahanadi Valley.
- The important issue fagged by the site inspection team was the threat to wild animals, especially elephants.
Coal Mining in Odisha
- Orissa is the second-largest state in terms of coal reserves, but it is also the third-largest coal producer, accounting for little over 15% of the country’s total coal production.
- Gondwana coal, a bituminous coal, is produced in Odisha.
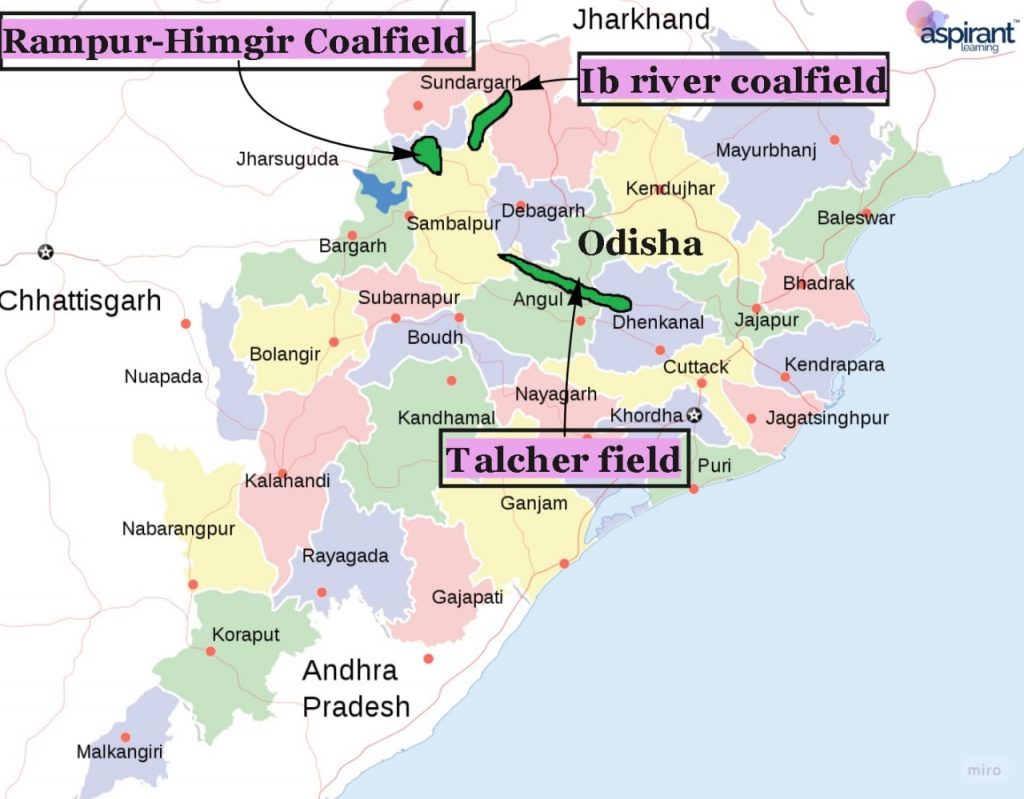
- The majority of the deposits are found in the districts of Dhenkanal, Sambalpur, and Sundargarh.
- After Raniganj, the Talcher field stretches eastward from Talcher town to Rairkhol in the Dhenkanal and Sambalpur districts. Talcher’s thermal power and fertiliser plants use the majority of the coal.
- Other coal deposits include the Rampur-Hemgir coalfields in Sambalpur’s districts. The lb river coalfield is located in the districts of Sambalpur and Gangpur.
Environmental Impacts Caused by Coal Mining
- Air Pollution:
- Blasting and drilling operations, coal fires, vehicular traffic, heavy trucks travelling on haul routes, coal loading and unloading, and wind erosion from overburden dumps are all major causes of air pollution.
- Oxides of nitrogen and sulphur, suspended particulate matter, respirable particulate matter, polyaromatic hydrocarbons, and benzene soluble matter are all important pollutants.
- Coal fires are also a significant problem.
- Water Pollution:
- Drainage from mining sites, sediment runoff from mining sites, erosion from overburden dumps and spoil heaps, leaking from tailing pond heating and heavy metals loaded effluents from coal companies, and sewage effluents are all major contributors of water pollution.
- Soil pollution:
- Strip mining pollutes the soil because it involves the removal of top soil, wind erosion from overburden dumps, coal heaps, tailing ponds, dust generated by heavy machinery used for extracting coal, coal burning, coal loading and unloading, and dust generated by heavy machinery used for extracting coal.
- Noise pollution
- Noise pollution is caused by the cumulative effect of various mining activities like blasting, drilling, crushing, and truck movement.
- Impact on Topography
- Clearing land for opencast mining, installing infrastructure connected to underground mining, depositing solid wastes in neighbouring areas, and subsidence due to fires can all cause changes in topography.
- Subsidence can result in the loss of infrastructure as well as a change in the area’s natural drainage pattern.
- Impact on biodiversity
- Vegetation destruction
- The vegetation pattern is affected by opencast and underground mining.
- The vegetation pattern changes, and there is a general rise in the area covered by sparse vegetation and barren ground.
- Habitat loss for animals due to forest clearance.
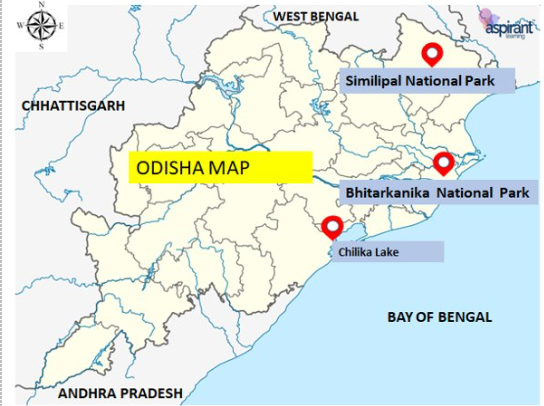
National parks of Odisha
Content Source : The Hindu



