Key Takeaways
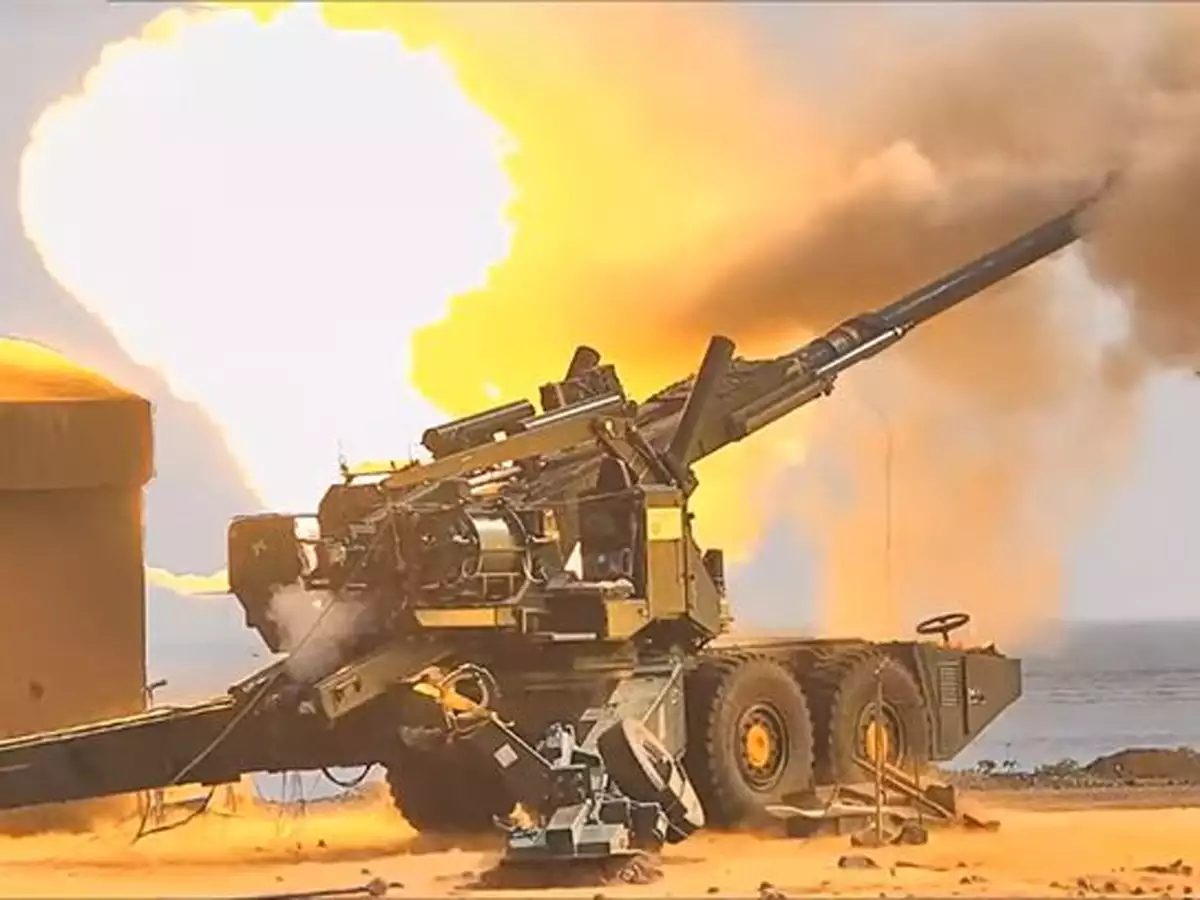
- Advanced Towed Artillery Gun System (ATAGS) crossed a milestone this week by successfully completing the validation trials towards meeting the specifications of the Army.
- The week-long Preliminary Service Quality Requirements (PSQR) validation retrials were conducted at the Pokhran field firing ranges from April 26 to May 2.
Background for Development of Advanced Towed Artillery Gun System (ATAGS)
- Since the Bofors (155 mm howitzer) in the 1980s, the Indian Army has not received a new artillery piece.
- The Army’s anticipated requirement for artillery weapons, including normal and advanced systems, is over 1,800.
- Army has also started receiving 155 mm Dhanush artillery pieces (an indigenously upgraded variant of the Bofors gun).
- Army has also been receiving modern artillery guns and equipment, such as the K9 Vajra (a partnership between South Korean and Indian businesses) and M777 howitzers (from the US).
- Army is also nearing completion on a deal to buy 400 Athos towed gun systems from Israeli firm Elbit Systems for Rs 5,147 crore.
When does ATAGS begin ?
- The development of ATAGS began in 2013 as part of the Indian Army’s artillery modernization program.
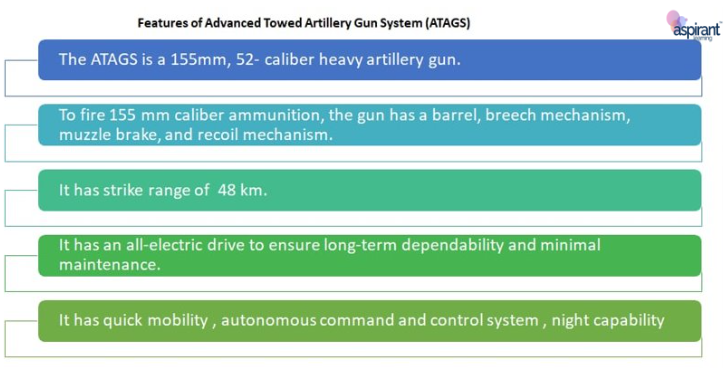
About Advanced Towed Artillery Gun System (ATAGS)
- It is an artillery gun jointly developed by Armament Research and Development Establishment (ARDE), the Pune-based laboratory of DRDO, in partnership with Bharat Forge and Tata Group.
- The indigenous content in ATAGS is larger than 95%.
Pic Courtesy: The New Indian Express
Content Source : The Hindu



