News Highlights
According to experts participating at the current fifth International Marine Protected Areas Congress, over 10 million square kilometres of the ocean must be placed under Marine Protected Areas (MPA) each year to safeguard 30% of the world’s ocean by 2030.
Key Takeaway:
- Countries set a target of protecting 30 per cent of the planet’s lands and oceans by 2030 at the 15th Conference of the Parties (COP15) to the Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD) held in 2022.
- MPAs represent only about 6 per cent of the ocean.
- MPAs currently make up only around 6% of the ocean. 2.4% are entirely and highly protected, and 3.6% are highly protected of this total. The remaining 0.8% are identified, and another 2% have been suggested and agreed upon.
Marine Protected Areas:
- About:
- A marine protected area (MPA) is a section of the ocean where a government has placed limits on human activity.
- Some governments ban fishing. A few do not allow people to enter the area at all.
- Many MPAs allow people to use the area in ways that do not damage the environment.
- Significance:
- MPAs have been established because the ocean and the things in it face many dangers. Threats to the ocean include overfishing, litter, water pollution, and global climate change.
- These threats have caused a decline in the population of many fish, marine mammals, and other sea creatures.
- Terminology:
- Marine protected areas can have many different names, including marine parks, marine conservation zones, marine reserves, marine sanctuaries, and no-take zones.
- More than 5,000 MPAs have been established around the world. Together, they cover 0.8 per cent of the ocean.
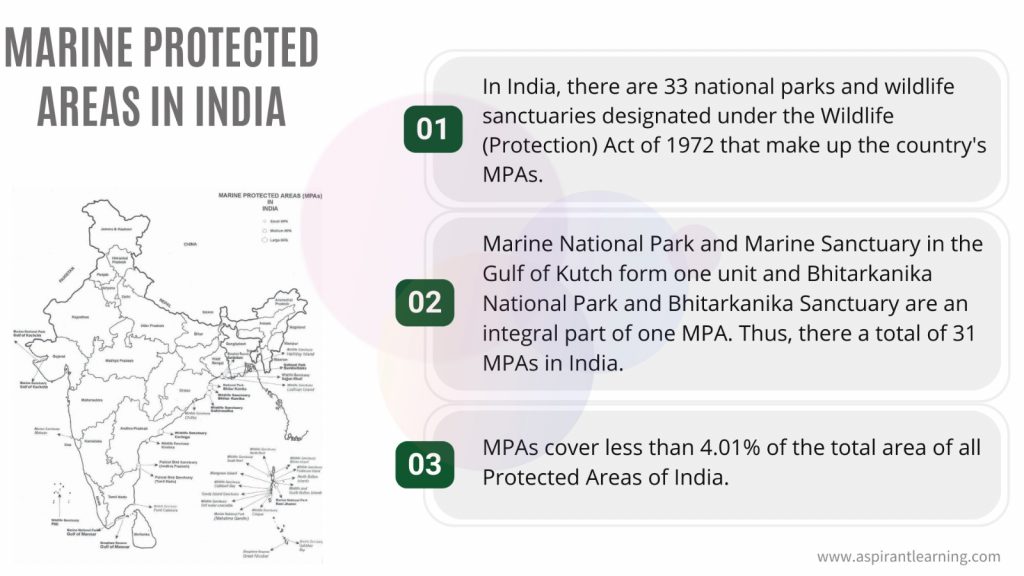
The necessity of creating MPAs:
- Conservation of biodiversity:
- The diversity of marine animals and their habitats are preserved by MPAs, helping to maintain the delicate balance of marine ecosystems and the services they offer, such as the generation of food and oxygen.
- Sustainable Fishing:
- To ensure that fish populations can recover and remain healthy, MPAs can assist in managing fishing activities and avoid overfishing, supporting sustainable fishing methods.
- Mitigation of Climate Change:
- By absorbing and storing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, MPAs can assist in lessening the effects of climate change on marine ecosystems.
- Research and Education:
- MPAs can offer beneficial chances for scientific study and educational endeavours, advancing knowledge about the marine environment and encouraging ocean awareness.
- Economic Benefits:
- By drawing tourists, offering possibilities for eco-friendly recreation and tourism, and aiding local fishing communities, MPAs can boost local economies.
International Marine Protected Areas Congress:
- About:
- IMPAC congresses are a collaborative effort between the International Union for the Conservation of Nature (IUCN) and the chosen host country.
- The congress brings scientists, policymakers, practitioners, and stakeholders from around the world to discuss the latest scientific knowledge, best practices and challenges in managing MPAs.
Pic Courtesy: Freepik
Content Source: Down To Earth



